Async/Await with forEach: A Practical Guide
Learn how to effectively use async/await with a forEach loop in JavaScript to handle asynchronous operations within loops and avoid potential pitfalls.
Learn how to effectively use async/await with a forEach loop in JavaScript to handle asynchronous operations within loops and avoid potential pitfalls.
In JavaScript, combining async/await with forEach can lead to unexpected outcomes due to the synchronous nature of forEach. While async/await is used for asynchronous operations, forEach executes each iteration immediately without waiting for asynchronous tasks to finish. This article explores alternative methods for handling asynchronous operations within loops, including using for...of with await for sequential processing, Promise.all with map for concurrent processing, traditional for loops with await and index access, and recursive functions with await for custom control flow. The choice of approach depends on the specific use case and desired behavior.
The core issue lies in how forEach operates. It's designed for synchronous tasks, meaning it executes each iteration immediately without waiting for any asynchronous operations to complete. When you introduce async/await within a forEach loop, the asynchronous tasks are initiated, but the loop continues without waiting for their results. This leads to unpredictable behavior and potential errors.
Here are several effective approaches to handle asynchronous operations within loops:
1. for...of Loop with await:
This method provides a clean and straightforward way to process asynchronous tasks sequentially.
async function processArray(array) {
for (const item of array) {
const result = await asyncOperation(item);
// Do something with the result
}
}2. Promise.all with map:
This approach is ideal when you want to execute asynchronous tasks concurrently and wait for all of them to finish before proceeding.
async function processArray(array) {
const promises = array.map(async (item) => {
const result = await asyncOperation(item);
return result;
});
const results = await Promise.all(promises);
// Do something with the results array
}3. for Loop with await and Index:
If you need the index of each item during asynchronous processing, you can use a traditional for loop with await.
async function processArray(array) {
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
const result = await asyncOperation(array[i]);
// Do something with the result and index i
}
}4. Recursive Function with await:
For scenarios where you need more control over the iteration flow, a recursive function with await can be helpful.
async function processArray(array, index = 0) {
if (index >= array.length) return;
const result = await asyncOperation(array[index]);
// Do something with the result
await processArray(array, index + 1);
}The best method depends on your specific use case:
for...of or a for loop with await.Promise.all with map.for loop with await and index.await.Remember to avoid using async/await directly within a forEach loop to prevent unexpected behavior and ensure your asynchronous operations are handled correctly.
The code demonstrates a common issue when using async/await with forEach. The forEach loop doesn't wait for asynchronous operations to complete before moving to the next iteration, leading to unexpected execution order. The provided alternatives, including using for...of loop with await, Promise.all with map, for loop with await and index, and recursive function with await, offer solutions to ensure proper handling of asynchronous operations within the loop. Each approach has its own advantages depending on the desired behavior, such as sequential processing, concurrent processing, index access, or custom control flow.
async function processArray(array) {
array.forEach(async (item) => {
const result = await asyncOperation(item);
console.log(result); // This may not execute in the expected order
});
console.log("Finished processing"); // This line might execute before all async operations complete
}
async function asyncOperation(item) {
// Simulate an asynchronous operation with a delay
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => resolve(item * 2), 1000);
});
}
processArray([1, 2, 3]);In this example, the console.log(result) within the forEach might not execute in the order you expect, and the "Finished processing" message could appear before all asynchronous operations are finished. This is because forEach doesn't wait for the await calls to complete before moving to the next iteration.
Here's how you can use the alternative approaches mentioned in the article:
1. for...of Loop with await:
async function processArray(array) {
for (const item of array) {
const result = await asyncOperation(item);
console.log(result);
}
console.log("Finished processing");
}2. Promise.all with map:
async function processArray(array) {
const results = await Promise.all(array.map(async (item) => {
return await asyncOperation(item);
}));
console.log(results); // Logs the results array
console.log("Finished processing");
}3. for Loop with await and Index:
async function processArray(array) {
for (let i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
const result = await asyncOperation(array[i]);
console.log(`Result at index ${i}: ${result}`);
}
console.log("Finished processing");
}4. Recursive Function with await:
async function processArray(array, index = 0) {
if (index >= array.length) {
console.log("Finished processing");
return;
}
const result = await asyncOperation(array[index]);
console.log(result);
await processArray(array, index + 1);
}Remember to choose the approach that best suits your needs based on whether you require sequential processing, concurrent processing, index access, or custom control flow.
try...catch blocks or error handling libraries to ensure robustness.| Method | Description |
|---|---|
for...of Loop with await
|
Processes asynchronous tasks sequentially in a clean and straightforward manner. |
Promise.all with map
|
Executes asynchronous tasks concurrently and waits for all to finish before proceeding. |
for Loop with await and Index |
Processes asynchronous tasks sequentially while providing access to the index of each item. |
Recursive Function with await
|
Offers more control over the iteration flow for complex asynchronous operations. |
By understanding the limitations of forEach with asynchronous operations and exploring alternative methods like for...of with await, Promise.all with map, and recursive functions, developers can write more predictable, efficient, and maintainable asynchronous code in JavaScript. The choice of approach depends on the specific requirements of the task, such as the need for sequential or concurrent processing, index access, or custom control flow. Additionally, considerations like error handling, performance optimization, cancellation, progress tracking, and the use of advanced techniques or libraries can further enhance the robustness and effectiveness of asynchronous operations in JavaScript applications.
 Do not use forEach with async-await · GitHub | Do not use forEach with async-await. GitHub Gist: instantly share code, notes, and snippets.
Do not use forEach with async-await · GitHub | Do not use forEach with async-await. GitHub Gist: instantly share code, notes, and snippets.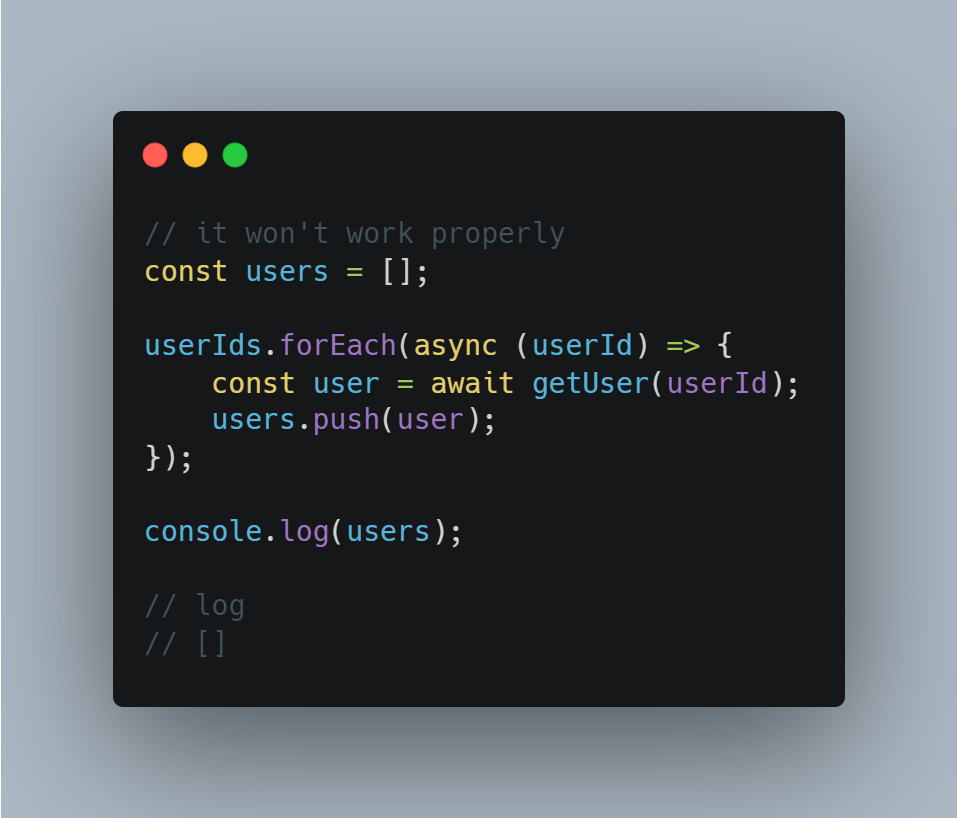 Using async/await in a forEach loop (you can't) | by David Okolo ... | I came across a complaint on how the forEach loop is inconsistent when you pass in an asynchronous lambda function as the callback argument…
Using async/await in a forEach loop (you can't) | by David Okolo ... | I came across a complaint on how the forEach loop is inconsistent when you pass in an asynchronous lambda function as the callback argument… How to use async/await with forEach loop in JavaScript ... | A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.
How to use async/await with forEach loop in JavaScript ... | A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions. Not awaiting query called in forEach loop - App Building - Retool ... | I'm likely missing something here, but am trying to call two update queries using a forEach loop, but need to wait until that loop is done before refreshing the page. I have tried using async await everywhere I can and calling refreshTable query on success of the javaScript query, but that didn't work either. The only thing I've had work is is the timeout function I have commented out. async function update1(item) { await updateQuery1.trigger({ additionalScope: { scope1: textBox.val...
Not awaiting query called in forEach loop - App Building - Retool ... | I'm likely missing something here, but am trying to call two update queries using a forEach loop, but need to wait until that loop is done before refreshing the page. I have tried using async await everywhere I can and calling refreshTable query on success of the javaScript query, but that didn't work either. The only thing I've had work is is the timeout function I have commented out. async function update1(item) { await updateQuery1.trigger({ additionalScope: { scope1: textBox.val... How to use async/await with a forEach loop in JavaScript? : r/javascript | Posted by u/stackthrive - No votes and 14 comments
How to use async/await with a forEach loop in JavaScript? : r/javascript | Posted by u/stackthrive - No votes and 14 comments Iterating Asynchronously: How to use async & await with foreach in ... | In this post, we will look at how we go about iterating using a foreach loop asynchronously. Now you may be thinking why do I need to know…
Iterating Asynchronously: How to use async & await with foreach in ... | In this post, we will look at how we go about iterating using a foreach loop asynchronously. Now you may be thinking why do I need to know…