Lower GCP Load Balancer Costs: Tips & Tricks
Learn how to optimize Google Cloud Platform (GCP) load balancer configurations and reduce costs associated with traffic management and application delivery.
Learn how to optimize Google Cloud Platform (GCP) load balancer configurations and reduce costs associated with traffic management and application delivery.
This article delves into the intricacies of Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Load Balancer costs, equipping you with the knowledge to understand, analyze, and optimize your expenses. We'll explore the various cost components, identify key drivers behind these costs, and present effective strategies for optimization. Additionally, we'll discuss cost-effective alternatives and provide a practical example of optimizing a JavaScript application using Cloud CDN. By understanding and implementing these insights, you can ensure efficient and cost-conscious utilization of GCP Load Balancers for your applications.
GCP Load Balancers offer powerful features for scaling and managing traffic, but their costs can sometimes be surprising. Let's explore ways to understand and optimize these costs:
1. Identifying Cost Components:
2. Analyzing Cost Drivers:
3. Optimization Strategies:
4. Cost-Effective Alternatives:
5. Example: Optimizing JavaScript Application with Cloud CDN
Here's how you can use Cloud CDN to optimize a JavaScript application:
// Configure Cloud CDN for static assets
const storage = require('@google-cloud/storage');
const bucketName = 'your-bucket-name';
async function enableCdn() {
const storageClient = new storage.Storage();
const bucket = storageClient.bucket(bucketName);
// Enable CDN for the bucket
await bucket.setMetadata({
cdnPolicy: {
enabled: true,
},
});
console.log(`CDN enabled for bucket ${bucketName}`);
}
enableCdn().catch(console.error);This code snippet demonstrates enabling Cloud CDN for a Cloud Storage bucket containing your JavaScript application's static assets. This can significantly reduce latency and network costs for users accessing your application.
Remember: Regularly review your load balancer configurations and traffic patterns to identify further optimization opportunities and ensure cost-efficiency.
This JavaScript code helps you save money on Google Cloud Platform (GCP) by using Cloud CDN to deliver content from a Cloud Storage bucket faster and cheaper. It uses the Node.js library for Google Cloud Storage to turn on Cloud CDN for your bucket, which stores static files like JavaScript, images, etc. This makes your website or application load faster for users around the world while reducing the cost of serving content from GCP.
This example demonstrates how to use the Node.js client library for Google Cloud Storage to enable Cloud CDN for a bucket containing static assets of your JavaScript application.
const {Storage} = require('@google-cloud/storage');
// Replace with your bucket name
const bucketName = 'your-bucket-name';
async function enableCDN() {
try {
// Creates a client
const storage = new Storage();
// Gets a reference to the bucket
const bucket = storage.bucket(bucketName);
// Enables CDN for the bucket
await bucket.setMetadata({
cdn: {
enabled: true,
},
});
console.log(`Cloud CDN enabled for bucket: ${bucketName}`);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error enabling Cloud CDN:', error);
}
}
enableCDN();Explanation:
Storage class from the @google-cloud/storage library to interact with Google Cloud Storage.'your-bucket-name' with the actual name of your Cloud Storage bucket where your static assets (JavaScript files, images, etc.) are stored.Storage class to interact with Cloud Storage.bucket() method.setMetadata() method to update the bucket's metadata and enable the cdn property.try...catch block to handle potential errors during the process.Additional Considerations:
Remember: This is a basic example. You can extend it to include more advanced features and configurations based on your application's requirements.
Remember: Cost optimization is an ongoing process. Regularly review your architecture, usage patterns, and GCP offerings to identify new opportunities for cost savings and efficiency improvements.
| Cost Components | Description |
|---|---|
| Data Processing | Charges for processing data, including request and response sizes. |
| Network Usage | Costs for data flowing through the load balancer (ingress and egress). |
| Forwarding Rules | Minimum charge per rule, even with minimal traffic. |
| Backend Instances | Costs based on instance type and quantity. |
| --- | --- |
| Cost Drivers | Description |
| Traffic Volume | Higher traffic increases data processing and network costs. |
| Global vs Regional | Global load balancers have higher forwarding rule charges. |
| Backend Instance Type | High-performance instances increase backend costs. |
| Idle Resources | Unused rules or over-provisioned instances lead to unnecessary expenses. |
| --- | --- |
| Optimization Strategies | Description |
| Right-Sizing Instances | Choose instances that meet needs without overspending; consider autoscaling. |
| Regional Load Balancers | Opt for regional ones to reduce forwarding rule costs if serving a specific region. |
| Optimizing Data Transfer | Minimize data transfer (e.g., compress responses, use caching, optimize application logic). |
| Cloud CDN | Cache static content closer to users, reducing backend load and network usage. |
| Monitoring and Alerting | Identify cost spikes and optimization opportunities. |
| --- | --- |
| Cost-Effective Alternatives | Description |
| Internal Load Balancers | Lower costs for internal traffic within your VPC. |
| Cloud Run | Serverless platform for stateless workloads; scales automatically and charges based on usage. |
| Kubernetes Ingress | Use Ingress controllers for basic load balancing in Kubernetes environments. |
Mastering GCP Load Balancer costs involves understanding the various cost components, identifying key drivers, and implementing effective optimization strategies. By carefully analyzing traffic patterns, right-sizing instances, leveraging regional load balancers and Cloud CDN, and exploring cost-effective alternatives, you can significantly reduce your expenses while maintaining optimal application performance. Remember, cost optimization is an ongoing process. Regularly review your architecture, usage patterns, and GCP offerings to identify new opportunities for cost savings and efficiency improvements. By adopting a proactive and informed approach, you can ensure that your GCP Load Balancers deliver both high performance and cost-effectiveness for your applications.
 Re: How to cut my GCP Load Balancer costs | Everything goes on well, but recently, I find every project will be charged on
Re: How to cut my GCP Load Balancer costs | Everything goes on well, but recently, I find every project will be charged on HTTP Load Balancing: Global Forwarding Rule Minimum Service Charge, almost 18 ...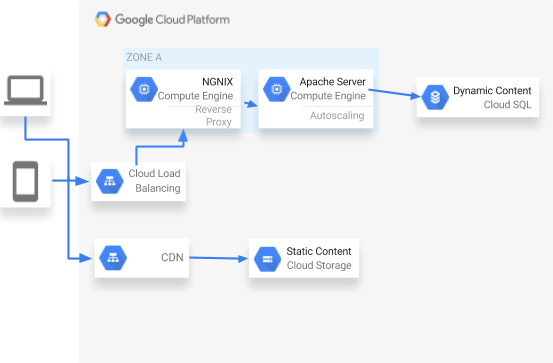 Removing the need for caching servers, with GCP's load balancers ... | Tax Lemming is a startup out of Vancouver, BC which focuses on helping you make sense of your purchases, taxes, and basic bookkeeping for…
Removing the need for caching servers, with GCP's load balancers ... | Tax Lemming is a startup out of Vancouver, BC which focuses on helping you make sense of your purchases, taxes, and basic bookkeeping for…