Python List Length: Find Number of Elements
Learn how to efficiently determine the number of elements in a Python list using the built-in len() function with practical examples.
Learn how to efficiently determine the number of elements in a Python list using the built-in len() function with practical examples.
In Python, determining the number of elements within a list is easily achievable using the built-in len() function. Let's break down how to utilize this function effectively.
To find the number of elements in a list in Python, you can use the built-in len() function.
Create a list:
my_list = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]Use the len() function:
list_length = len(my_list)Print the result:
print(list_length) # Output: 3In this example, len(my_list) returns the length of the list my_list, which is 3. This value is then stored in the variable list_length and printed to the console.
This Python code demonstrates how to find the length of a list. It first defines a list of fruits, then uses the len() function to determine the number of elements in the list. Finally, it prints the length of the list to the console.
# Create a list of fruits
my_list = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
# Get the length of the list using the len() function
list_length = len(my_list)
# Print the length of the list
print("The length of the list is:", list_length) Output:
The length of the list is: 3
Explanation:
my_list = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]: This line creates a list named my_list containing three string elements: "apple", "banana", and "cherry".
list_length = len(my_list): This line uses the len() function to determine the number of elements in my_list. The result, which is 3 in this case, is then assigned to the variable list_length.
print("The length of the list is:", list_length): This line prints a descriptive message followed by the value stored in list_length, effectively displaying the length of the list to the user.
Versatility of len(): The len() function isn't limited to lists. You can use it to find the length of other data structures like strings, tuples, dictionaries, and sets.
Importance in Programming: Knowing the length of a list is crucial for tasks like:
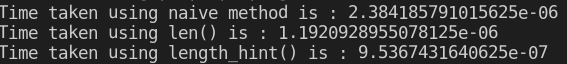
for loop.Alternatives to len(): While len() is the most common and efficient way, you can also find the length of a list using loops. However, this is generally less efficient and not the recommended approach.
Zero-Based Indexing: Remember that Python uses zero-based indexing. This means the first element of a list has an index of 0, the second has an index of 1, and so on. The last element's index is the length of the list minus 1.
Error Handling: If you try to use len() on a variable that isn't a sequence (like an integer or a float), you'll get a TypeError. It's good practice to include error handling in your code if you're unsure about the data type you're working with.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Finding List Length | Use the len() function. |
| Example |
len(["apple", "banana", "cherry"]) returns 3. |
| Explanation | The len() function directly returns the number of elements in a list. |
The len() function in Python provides a straightforward and efficient method for determining the number of elements in a list. This function is essential for various programming tasks, including iterating through lists, validating data, and dynamic memory allocation. Understanding how to use len() effectively is fundamental for Python programmers.
 How To Find the Length of a List in Python - GeeksforGeeks | A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.
How To Find the Length of a List in Python - GeeksforGeeks | A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions. How to Get the Length of a List in Python | Cherry Servers | Learn how to get the length of a Python list by using len(), for loop, length_hint(), len() methods and NumPy library.
How to Get the Length of a List in Python | Cherry Servers | Learn how to get the length of a Python list by using len(), for loop, length_hint(), len() methods and NumPy library. Finding the Length of a List in Python (With Examples) | Determining the length of a list has many use cases when scripting data processing and analysis tasks, especially for us at IOFLOOD. As we have gotten
Finding the Length of a List in Python (With Examples) | Determining the length of a list has many use cases when scripting data processing and analysis tasks, especially for us at IOFLOOD. As we have gotten How to Find List Length in Python {3 Methods} | phoenixNAP KB | Don't know how many elements are in a list? This guide shows you three different ways to find the length of a list in Python!
How to Find List Length in Python {3 Methods} | phoenixNAP KB | Don't know how many elements are in a list? This guide shows you three different ways to find the length of a list in Python! Python List Length | W3Schools offers free online tutorials, references and exercises in all the major languages of the web. Covering popular subjects like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Python, SQL, Java, and many, many more.
Python List Length | W3Schools offers free online tutorials, references and exercises in all the major languages of the web. Covering popular subjects like HTML, CSS, JavaScript, Python, SQL, Java, and many, many more. What is the easiest way to access the last element of a list? - Python ... | Question Is there a way to find the last item in a list without using the len() function? Answer The last item in a list can be found using the index value computed by len() - 1 for the list. A short-hand for this is to use an index value of -1. For any list, accessing the index of [-1] will return the last element of the list without needing to use the len() function. In the example below, both print() functions will output orange for the color. colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'yellow', 'o...
What is the easiest way to access the last element of a list? - Python ... | Question Is there a way to find the last item in a list without using the len() function? Answer The last item in a list can be found using the index value computed by len() - 1 for the list. A short-hand for this is to use an index value of -1. For any list, accessing the index of [-1] will return the last element of the list without needing to use the len() function. In the example below, both print() functions will output orange for the color. colors = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'yellow', 'o... ee.List.length | Google Earth Engine | Google for Developers | Oct 6, 2023 ... Returns the number of elements in list. Was this helpful? Send feedback Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under the Creative ...
ee.List.length | Google Earth Engine | Google for Developers | Oct 6, 2023 ... Returns the number of elements in list. Was this helpful? Send feedback Except as otherwise noted, the content of this page is licensed under the Creative ...