Node.js Object Mapping: Beyond Arrays
Learn how to use the map function in Node.js to manipulate and transform objects, enabling efficient data processing and streamlined object-oriented programming.
Learn how to use the map function in Node.js to manipulate and transform objects, enabling efficient data processing and streamlined object-oriented programming.
Although JavaScript provides the handy .map() function for manipulating arrays, it falls short when dealing with objects. However, we can bridge this gap by cleverly combining existing methods to achieve a similar "map-like" functionality for objects. Let's explore a step-by-step approach to accomplish this.
While JavaScript's built-in .map() function works wonders for arrays, it doesn't directly apply to objects. However, we can achieve similar functionality by combining existing methods and techniques. Here's a step-by-step guide:
1. Understanding the Goal:
2. Extracting Key-Value Pairs:
Object.entries(obj) to get an array of key-value pairs. Each pair is represented as an array [key, value].const myObject = { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 };
const entries = Object.entries(myObject);
// entries = [ ['a', 1], ['b', 2], ['c', 3] ]3. Transforming Values:
.map() function on the entries array..map() callback, access the key and value from each pair.value.const transformedEntries = entries.map(([key, value]) => {
const newValue = transformFunction(value); // Your custom function
return [key, newValue];
});4. Creating a New Object:
Object.fromEntries(transformedEntries) to convert the transformed array back into an object.const newObject = Object.fromEntries(transformedEntries);Example: Doubling Values
function doubleValue(value) {
return value * 2;
}
const myObject = { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 };
const doubledObject = Object.fromEntries(
Object.entries(myObject).map(([key, value]) => [key, doubleValue(value)])
);
console.log(doubledObject); // Output: { a: 2, b: 4, c: 6 }Additional Considerations:
Promise.all() within the .map() callback to handle the asynchronous operations before creating the new object.In conclusion, while JavaScript doesn't have a direct equivalent to .map() for objects, we can achieve similar results by combining Object.entries(), .map(), and Object.fromEntries(). This allows us to iterate over key-value pairs, transform values, and create new objects with ease.
The JavaScript code defines a function 'doubleValue' that doubles a given value. It then creates an object 'myObject' with properties 'a', 'b', and 'c' having values 1, 2, and 3 respectively. The code then uses 'Object.entries', 'map', and 'Object.fromEntries' to create a new object 'doubledObject' where each value from 'myObject' is doubled using the 'doubleValue' function. Finally, it prints the 'doubledObject' which contains the doubled values { a: 2, b: 4, c: 6 }.
// Function to transform values (example: doubling)
function doubleValue(value) {
return value * 2;
}
// Sample object
const myObject = { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 };
// Applying the "map-like" operation
const doubledObject = Object.fromEntries(
Object.entries(myObject).map(([key, value]) => [key, doubleValue(value)])
);
// Output: { a: 2, b: 4, c: 6 }
console.log(doubledObject);Object.entries() is a common choice, you can also explore other methods like Object.keys() or Object.values() depending on your specific needs. For instance, if you only require the keys, Object.keys() would be more efficient.for...in loops might offer slight performance improvements in certain scenarios. However, it's essential to benchmark and compare based on your specific use case.| Step | Description | Code Example |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Goal | - Iterate over key-value pairs in an object. - Transform values using a function. - Create a new object with transformed values. | N/A |
| 2. Extract Pairs | - Use Object.entries(obj) to get an array of [key, value] pairs. |
const entries = Object.entries(myObject); |
| 3. Transform Values | - Use .map() on the entries array. - Apply transformation function to each value. - Return new [key, newValue] pairs. |
entries.map(([key, value]) => [key, transformFunction(value)]) |
| 4. Create New Object | - Use Object.fromEntries() to convert the transformed array back into an object. |
const newObject = Object.fromEntries(transformedEntries); |
In conclusion, while JavaScript doesn't have a direct equivalent to .map() for objects, we can achieve similar results by combining Object.entries(), .map(), and Object.fromEntries(). This allows us to iterate over key-value pairs, transform values, and create new objects with ease. This technique empowers developers to work with objects in a more functional and concise manner, enhancing code readability and maintainability. By understanding these methods and their combined power, you can unlock new possibilities for manipulating and transforming objects in your JavaScript projects.
 Map function for objects (instead of arrays) | Sentry | The Problem You have an object that you want to map over. Suppose you want to map over the following object and double each value: With an array, you can use…
Map function for objects (instead of arrays) | Sentry | The Problem You have an object that you want to map over. Suppose you want to map over the following object and double each value: With an array, you can use… Array.prototype.map() - JavaScript | MDN | The map() method of Array instances creates
a new array populated with the results of calling a provided function on
every element in the calling array.
Array.prototype.map() - JavaScript | MDN | The map() method of Array instances creates
a new array populated with the results of calling a provided function on
every element in the calling array. How To Use JavaScript Maps - .map() | DigitalOcean | One of the most popular methods of iterating through datasets in JavaScript is the .map() method. .map() creates an array from calling a specific functio…
How To Use JavaScript Maps - .map() | DigitalOcean | One of the most popular methods of iterating through datasets in JavaScript is the .map() method. .map() creates an array from calling a specific functio… Mapping an array within a mapped array? - JavaScript - The ... | I have an array of objects in my state called ‘ideas’. Each object in the array has a property called ‘premises’, and that property is an array. I’m trying to map through ideas, and within the function map through the premises of each idea, but it doesn’t seem to be working - idea.premises is supposedly undefined. What am I doing wrong? Should I be doing this a different way anyway? {this.state.ideas.map(idea => {
Mapping an array within a mapped array? - JavaScript - The ... | I have an array of objects in my state called ‘ideas’. Each object in the array has a property called ‘premises’, and that property is an array. I’m trying to map through ideas, and within the function map through the premises of each idea, but it doesn’t seem to be working - idea.premises is supposedly undefined. What am I doing wrong? Should I be doing this a different way anyway? {this.state.ideas.map(idea => { 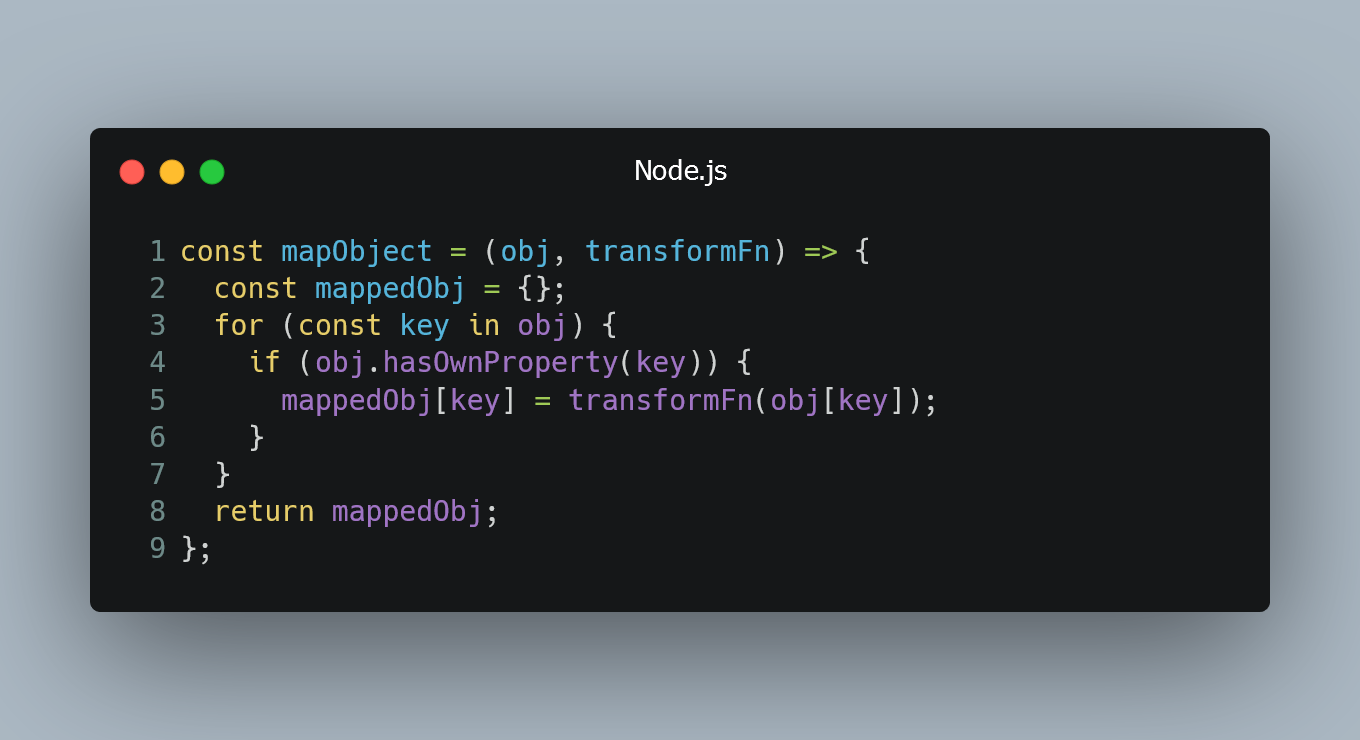 Map Function for Objects (Instead of Arrays) - Tiloid | In JavaScript, the map function is commonly used with arrays to transform elements and create new arrays based on the existing ones. However, there is...
Map Function for Objects (Instead of Arrays) - Tiloid | In JavaScript, the map function is commonly used with arrays to transform elements and create new arrays based on the existing ones. However, there is...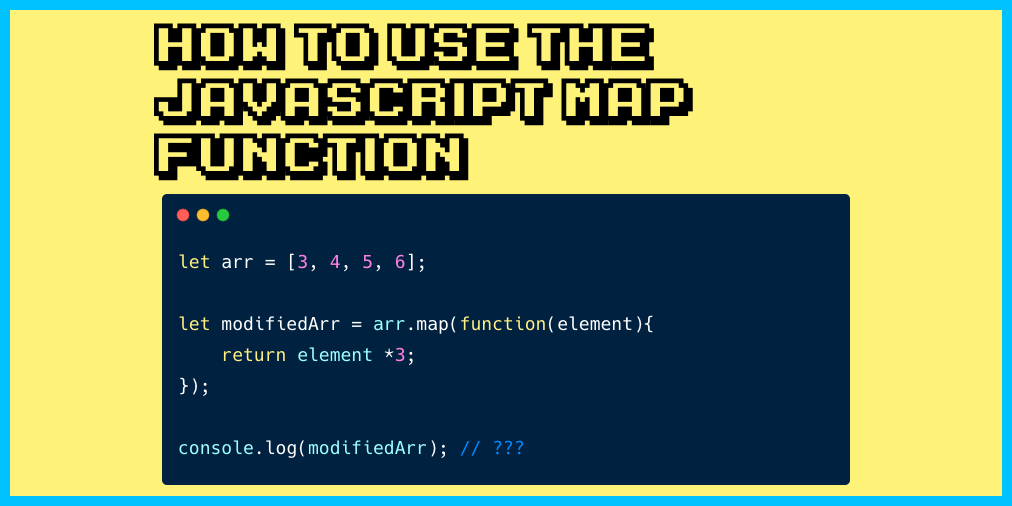 JavaScript Map – How to Use the JS .map() Function (Array Method) | Sometimes you may need to take an array and apply some procedure to its elements so that you get a new array with modified elements. Instead of manually iterating over the array using a loop, you can simply use the built-in Array.map() method. Here's an Interactive Scrim of How
JavaScript Map – How to Use the JS .map() Function (Array Method) | Sometimes you may need to take an array and apply some procedure to its elements so that you get a new array with modified elements. Instead of manually iterating over the array using a loop, you can simply use the built-in Array.map() method. Here's an Interactive Scrim of How map function for objects instead of arrays | Exploring the Map Function for Objects in JavaScript: A Developer's Guide
map function for objects instead of arrays | Exploring the Map Function for Objects in JavaScript: A Developer's Guide