How to Debounce in JavaScript
Learn how to implement debouncing techniques to improve performance and prevent unintended behavior triggered by rapid user interactions or events in your code.
Learn how to implement debouncing techniques to improve performance and prevent unintended behavior triggered by rapid user interactions or events in your code.
In the realm of JavaScript, where events occur with lightning speed, a technique known as debouncing emerges as a guardian of efficiency. Imagine a scenario where every keystroke triggers a flurry of activity, overwhelming your application with unnecessary tasks. Debouncing steps in to restore order, ensuring that functions are executed only when necessary, preventing performance bottlenecks and creating a seamless user experience. Join us on a journey to unravel the mysteries of debouncing, where we'll explore its inner workings and unveil its practical applications. Through step-by-step explanations and illustrative code examples, we'll equip you with the knowledge to harness the power of debouncing and elevate your JavaScript skills to new heights.
Debouncing is a powerful technique in JavaScript that limits the rate at which a function is executed. This is particularly useful for handling events that fire rapidly, such as scrolling, resizing, or typing in an input field. By debouncing, we ensure that the function is only called once after a certain period of inactivity, preventing performance issues and unwanted behavior.
Here's a step-by-step breakdown of how to implement debounce in JavaScript:
1. The Problem:
Imagine you have an input field where users can type to search for something. Every keystroke triggers an event that calls a function to fetch search results. If the user types quickly, this function will be called numerous times, leading to unnecessary network requests and a poor user experience.
2. The Solution: Debounce
Debouncing helps by delaying the function call until a certain amount of time has passed since the last event trigger. This way, the function is only executed once the user has finished typing, ensuring efficiency and a smoother experience.
3. Implementing Debounce:
Here's a basic JavaScript code example to demonstrate debouncing:
function debounce(func, delay) {
let timeoutId;
return function(...args) {
clearTimeout(timeoutId);
timeoutId = setTimeout(() => func.apply(this, args), delay);
};
}
// Example usage:
const searchInput = document.getElementById('search');
const searchFunction = (query) => {
// Perform search logic here
console.log('Searching for:', query);
};
const debouncedSearch = debounce(searchFunction, 300); // Debounce with 300ms delay
searchInput.addEventListener('keyup', (event) => {
debouncedSearch(event.target.value);
});Explanation:
debounce function:
func) and the delay in milliseconds (delay).timeoutId variable.clearTimeout.setTimeout that will execute the original function (func) after the specified delay.searchFunction that represents the actual search logic.searchFunction using the debounce function with a 300ms delay.keyup event of the search input.debouncedSearch function is called with the current input value.4. Benefits of Debouncing:
5. Use Cases:
By understanding and implementing debounce, you can significantly improve the performance and user experience of your JavaScript applications.
The JavaScript code defines a debounce function that limits the rate at which a given function can be executed. It's used to optimize performance by preventing a function from being called too frequently, such as during user input events like typing in a search bar. The example demonstrates how to debounce a search function to reduce unnecessary API calls while the user is still typing.
function debounce(func, delay) {
let timeoutId;
return function(...args) {
clearTimeout(timeoutId);
timeoutId = setTimeout(() => func.apply(this, args), delay);
};
}
// Example: Debouncing a search input
const searchInput = document.getElementById('search');
const searchFunction = (query) => {
console.log('Searching for:', query);
// Perform actual search logic here (e.g., fetch results)
};
const debouncedSearch = debounce(searchFunction, 300); // 300ms delay
searchInput.addEventListener('keyup', (event) => {
debouncedSearch(event.target.value);
});Explanation:
debounce Function:
func) and the delay in milliseconds (delay) as arguments.timeoutId of the scheduled function execution.clearTimeout(timeoutId) to prevent the function from being called prematurely.setTimeout that will execute the original func after the specified delay. The apply(this, args) ensures that func is called with the correct context (this) and arguments (args).Example Usage:
document.getElementById.searchFunction represents the actual search logic that would typically fetch and display results.debouncedSearch is created by calling the debounce function with searchFunction and a delay of 300 milliseconds.keyup event of the search input. Each time the user releases a key, the debouncedSearch function is called with the current input value.How it Works:
keyup event fires repeatedly.debouncedSearch function ensures that the searchFunction is only executed after the user has stopped typing for at least 300 milliseconds. This prevents unnecessary API calls or search operations while the user is still typing.Beyond the Basics:
setTimeout and calling clearTimeout on it when necessary.Advanced Implementations:
requestAnimationFrame: For tasks related to animation or visual updates, consider using requestAnimationFrame within the debounce function to ensure smooth and efficient rendering.Libraries and Frameworks:
debounceTime and throttleTime for handling event streams with debouncing and throttling.Real-World Applications:
Remember:
By mastering debounce, you'll gain a valuable tool for creating efficient and user-friendly JavaScript applications.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Problem | Frequent events (e.g., typing, scrolling) trigger excessive function calls, impacting performance and user experience. |
| Solution | Debounce: Limits function execution rate by delaying it until a specified inactivity period. |
| Implementation | - debounce(func, delay) function manages timeouts to control function calls. - Example: Debounced search function only executes after user finishes typing. |
| Benefits | - Improved performance and resource utilization. - Enhanced user experience with smoother interactions. - Controlled function execution timing. |
| Use Cases | - Search input suggestions - Auto-save functionality - Window resize events - Scroll events (e.g., lazy loading) |
As we conclude our exploration of debouncing in JavaScript, it becomes evident that this technique is an indispensable tool for any developer seeking to create responsive and efficient web applications. By strategically delaying function execution, debouncing empowers us to tame the flurry of events that can overwhelm our code, leading to performance bottlenecks and a frustrating user experience. Whether it's optimizing search input suggestions, implementing auto-save functionality, or handling window resize events, debouncing provides a simple yet powerful solution. It allows us to strike a balance between responsiveness and resource utilization, ensuring that our applications remain smooth and performant even under heavy event loads. Armed with the knowledge of debouncing, you are now equipped to tackle a wide range of challenges in your JavaScript projects. So, embrace this technique, experiment with its various implementations, and witness the transformation it brings to your web development endeavors. Remember, a well-placed debounce can make all the difference in creating an exceptional user experience.
 Debouncing in JavaScript – Explained by Building Auto-Complete ... | Hi readers, I hope you are doing great! I am back with another tutorial on web development. If you are someone who enjoys developing web apps with JavaScript and React, then this post is for you. When you roll out a new app into production, you want to make sure
Debouncing in JavaScript – Explained by Building Auto-Complete ... | Hi readers, I hope you are doing great! I am back with another tutorial on web development. If you are someone who enjoys developing web apps with JavaScript and React, then this post is for you. When you roll out a new app into production, you want to make sure Debouncing in JavaScript - GeeksforGeeks | A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.
Debouncing in JavaScript - GeeksforGeeks | A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions. Debounce – How to Delay a Function in JavaScript (JS ES6 Example) | In JavaScript, a debounce function makes sure that your code is only triggered once per user input. Search box suggestions, text-field auto-saves, and eliminating double-button clicks are all use cases for debounce. In this tutorial, we'll learn how to create a debounce function in JavaScript. What is debounce? The
Debounce – How to Delay a Function in JavaScript (JS ES6 Example) | In JavaScript, a debounce function makes sure that your code is only triggered once per user input. Search box suggestions, text-field auto-saves, and eliminating double-button clicks are all use cases for debounce. In this tutorial, we'll learn how to create a debounce function in JavaScript. What is debounce? The Best way to do a debounce - Code Review - Developer Forum ... | Hi, I am making my input script and I was wondering what is the best way to do a debounce since my debounces are very ugly and standard. If you have any particular different method please comment it Thanks for reading 🙂 local ReplicatedStorage = game:GetService("ReplicatedStorage") local ContextActionUility = require(ReplicatedStorage.Modules.ContextActionUtility) local TweenService = game:GetService("TweenService") local Players = game:GetService("Players") local RunService = ga...
Best way to do a debounce - Code Review - Developer Forum ... | Hi, I am making my input script and I was wondering what is the best way to do a debounce since my debounces are very ugly and standard. If you have any particular different method please comment it Thanks for reading 🙂 local ReplicatedStorage = game:GetService("ReplicatedStorage") local ContextActionUility = require(ReplicatedStorage.Modules.ContextActionUtility) local TweenService = game:GetService("TweenService") local Players = game:GetService("Players") local RunService = ga...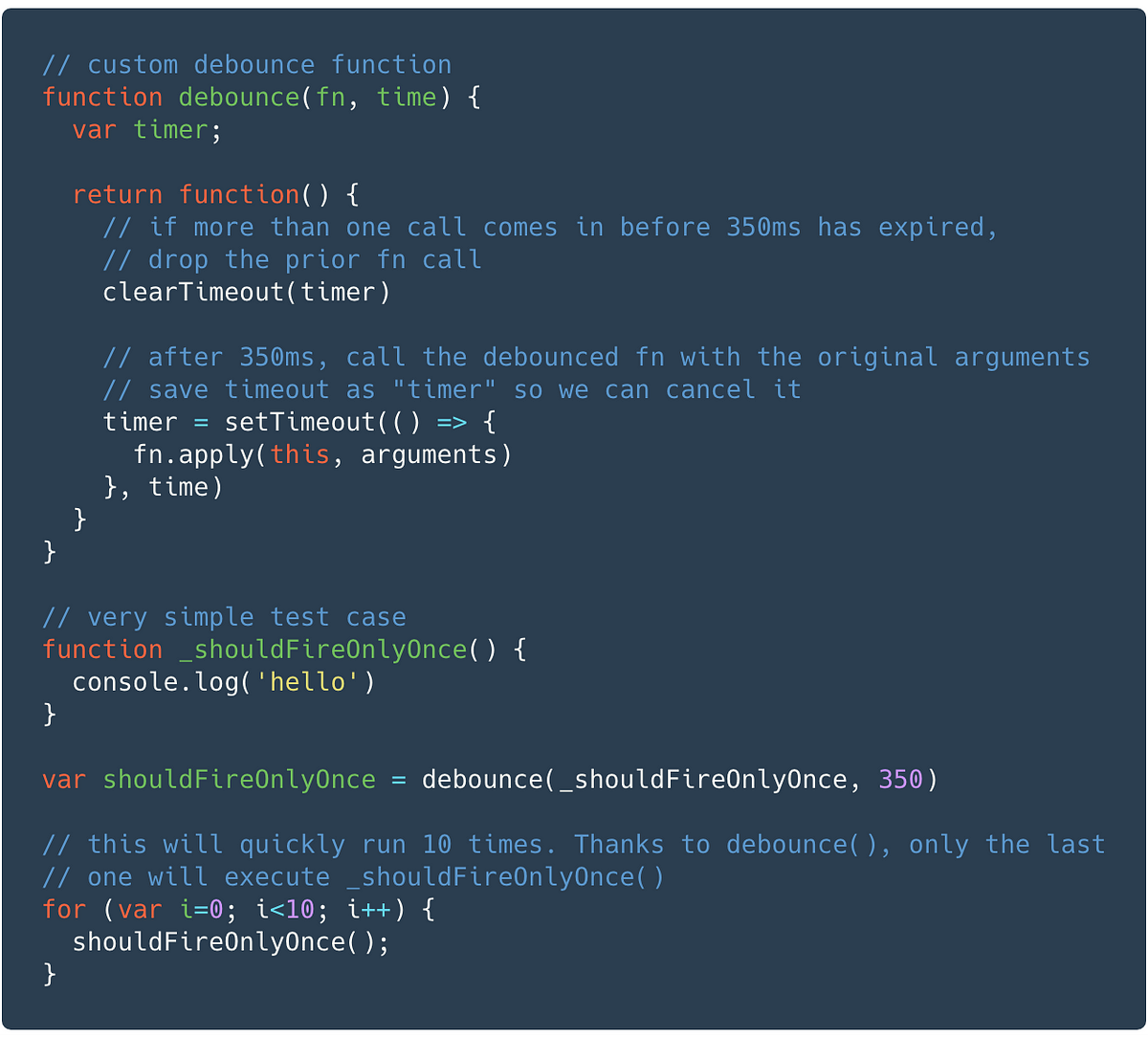 What is Debouncing?. Debouncing is something that comes up ... | Debouncing is something that comes up fairly frequently in UI development. In the last few years I’ve encountered several interview…
What is Debouncing?. Debouncing is something that comes up ... | Debouncing is something that comes up fairly frequently in UI development. In the last few years I’ve encountered several interview… How Would I Make A Debounce For This Animation Script - Scripting ... | local Player = game.Players.LocalPlayer local Mouse = Player:GetMouse() Mouse.KeyDown:connect(function(key) if key == “f” then local an = script.Parent.Humanoid:LoadAnimation(script.Animation) an:Play() script.Parent.RightHand.Touched:connect(function(hit) if hit.Parent.Humanoid == true then hit.Parent.Humanoid:TakeDamage(Player.leaderstats.Strength.Value) end end) end end)
How Would I Make A Debounce For This Animation Script - Scripting ... | local Player = game.Players.LocalPlayer local Mouse = Player:GetMouse() Mouse.KeyDown:connect(function(key) if key == “f” then local an = script.Parent.Humanoid:LoadAnimation(script.Animation) an:Play() script.Parent.RightHand.Touched:connect(function(hit) if hit.Parent.Humanoid == true then hit.Parent.Humanoid:TakeDamage(Player.leaderstats.Strength.Value) end end) end end) JavaScript Debounce, Easiest explanation !(with Code) - DEV ... | Debouncing is a programming technique that helps to improve the performance of web applications by...
JavaScript Debounce, Easiest explanation !(with Code) - DEV ... | Debouncing is a programming technique that helps to improve the performance of web applications by... What is debounce - Scripting Support - Developer Forum | Roblox | So in every YT tutorial, I see this line where they set a variable called debounce, and set it to false. But why do they do that? What does it do?
What is debounce - Scripting Support - Developer Forum | Roblox | So in every YT tutorial, I see this line where they set a variable called debounce, and set it to false. But why do they do that? What does it do?