Bounding Box Overlap Percentage: Image Detector Evaluation
Learn how to calculate the percentage of bounding box overlap, a crucial metric for evaluating the accuracy of object detection models in computer vision tasks.
Learn how to calculate the percentage of bounding box overlap, a crucial metric for evaluating the accuracy of object detection models in computer vision tasks.
Intersection over Union (IoU), a crucial concept in object detection tasks, quantifies the extent of overlap between two bounding boxes. This measure finds applications in evaluating the accuracy of object detection models and assessing the degree of alignment between predicted and ground truth bounding boxes. This article provides a step-by-step guide to calculating the IoU, guiding you through the process of determining the overlap between two bounding boxes.
To calculate the percentage of bounding box overlap, also known as Intersection over Union (IoU), follow these steps:
Define the bounding boxes:
bbox1 = [x1_min, y1_min, x1_max, y1_max]
bbox2 = [x2_min, y2_min, x2_max, y2_max]Calculate the coordinates of the intersection rectangle:
intersection_x_min = max(x1_min, x2_min)
intersection_y_min = max(y1_min, y2_min)
intersection_x_max = min(x1_max, x2_max)
intersection_y_max = min(y1_max, y2_max)Calculate the area of the intersection rectangle:
intersection_area = max(0, intersection_x_max - intersection_x_min) * max(0, intersection_y_max - intersection_y_min)Calculate the area of each bounding box:
bbox1_area = (x1_max - x1_min) * (y1_max - y1_min)
bbox2_area = (x2_max - x2_min) * (y2_max - y2_min)Calculate the area of the union of the two bounding boxes:
union_area = bbox1_area + bbox2_area - intersection_areaCalculate the IoU:
iou = intersection_area / union_areaThe IoU value ranges from 0 to 1, where 0 indicates no overlap and 1 indicates perfect overlap.
This Python code calculates the Intersection over Union (IoU) for two given bounding boxes. It defines a function calculate_iou that takes the coordinates of two bounding boxes as input and returns their IoU value, a float between 0 and 1. The code also includes an example usage demonstrating how to use the function with sample bounding box data.
def calculate_iou(bbox1, bbox2):
"""Calculates the Intersection over Union (IoU) of two bounding boxes.
Args:
bbox1: A list of coordinates representing the first bounding box
in the format [x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max].
bbox2: A list of coordinates representing the second bounding box
in the format [x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max].
Returns:
The IoU value, a float between 0 and 1.
"""
# Calculate the coordinates of the intersection rectangle
intersection_x_min = max(bbox1[0], bbox2[0])
intersection_y_min = max(bbox1[1], bbox2[1])
intersection_x_max = min(bbox1[2], bbox2[2])
intersection_y_max = min(bbox1[3], bbox2[3])
# Calculate the area of the intersection rectangle
intersection_area = max(0, intersection_x_max - intersection_x_min) * max(0, intersection_y_max - intersection_y_min)
# Calculate the area of each bounding box
bbox1_area = (bbox1[2] - bbox1[0]) * (bbox1[3] - bbox1[1])
bbox2_area = (bbox2[2] - bbox2[0]) * (bbox2[3] - bbox2[1])
# Calculate the area of the union of the two bounding boxes
union_area = bbox1_area + bbox2_area - intersection_area
# Calculate the IoU
iou = intersection_area / union_area
return iou
# Example usage:
bbox1 = [10, 10, 50, 50]
bbox2 = [20, 20, 60, 60]
iou = calculate_iou(bbox1, bbox2)
print(f"IoU: {iou}")This code defines a function calculate_iou that takes two bounding boxes as input and returns their IoU. The function follows the steps outlined in the article to calculate the intersection area, union area, and finally the IoU. The example usage demonstrates how to use the function with two sample bounding boxes.
Understanding the Importance:
Considerations:
Applications Beyond Object Detection:
Visualizing IoU:
This summary outlines the steps to calculate IoU, a metric ranging from 0 to 1 that quantifies the overlap between two bounding boxes.
| Step | Description | Formula |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Define Bounding Boxes | Represent each box with its minimum and maximum x and y coordinates. | bbox = [x_min, y_min, x_max, y_max] |
| 2. Find Intersection Coordinates | Determine the coordinates of the rectangle where the two boxes overlap. |
intersection_x_min = max(x1_min, x2_min), etc. |
| 3. Calculate Intersection Area | Compute the area of the overlapping rectangle. | intersection_area = max(0, intersection_x_max - intersection_x_min) * max(0, intersection_y_max - intersection_y_min) |
| 4. Calculate Individual Box Areas | Calculate the area of each bounding box separately. | bbox_area = (x_max - x_min) * (y_max - y_min) |
| 5. Calculate Union Area | Determine the total area covered by both boxes, avoiding double-counting the intersection. | union_area = bbox1_area + bbox2_area - intersection_area |
| 6. Calculate IoU | Divide the intersection area by the union area to obtain the IoU. | iou = intersection_area / union_area |
Interpretation:
In conclusion, IoU serves as a fundamental metric for assessing the accuracy of object detection and related computer vision tasks. By quantifying the degree of overlap between predicted and ground truth bounding boxes, IoU provides a valuable measure for evaluating model performance. The provided Python code offers a practical implementation for calculating IoU, enabling developers and researchers to integrate this metric into their workflows. Understanding IoU and its applications is essential for anyone involved in object detection, image segmentation, or tracking, as it provides a standardized and interpretable way to assess the effectiveness of algorithms in these domains.
 Calculate Percentage of Bounding Box Overlap, for Image Detector ... | A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.
Calculate Percentage of Bounding Box Overlap, for Image Detector ... | A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.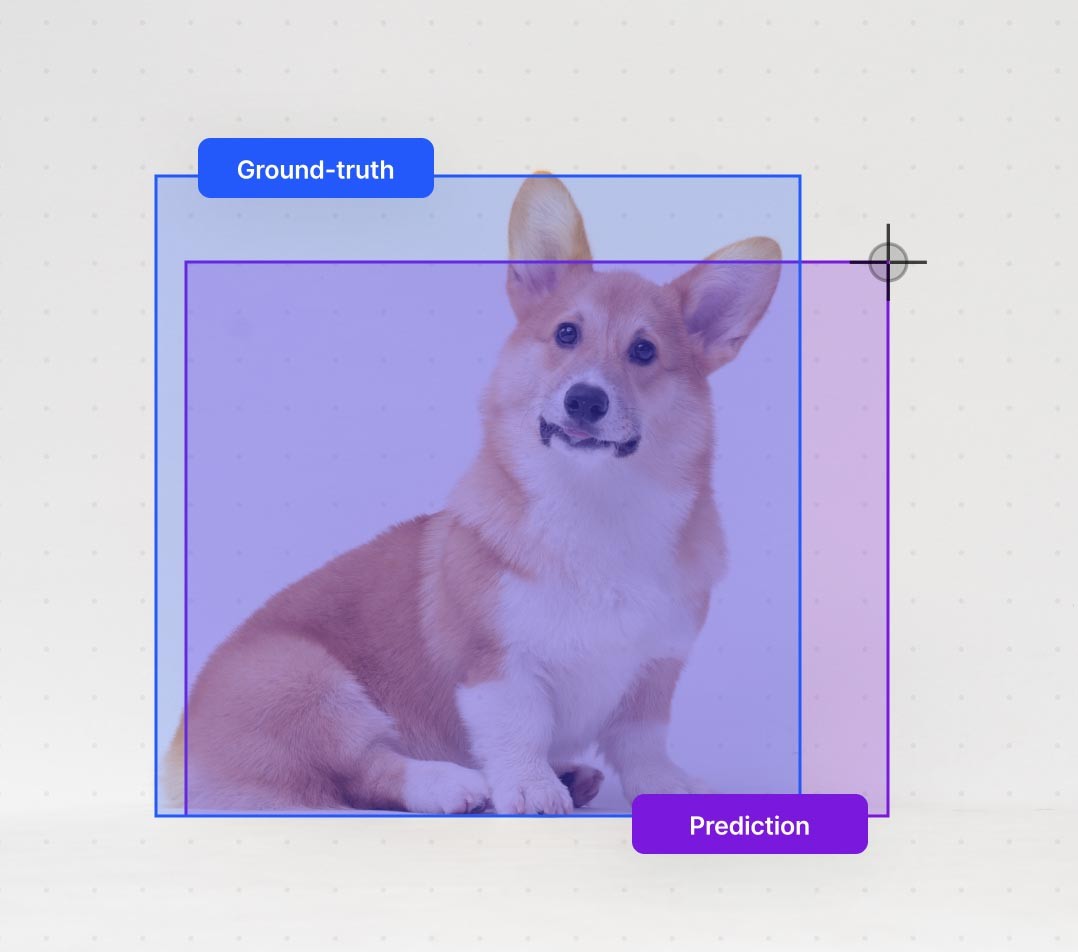 Intersection over Union (IoU): Definition, Calculation, Code | Find out how and when to use IoU, one of the most crucial model model assessment metrics.
Intersection over Union (IoU): Definition, Calculation, Code | Find out how and when to use IoU, one of the most crucial model model assessment metrics.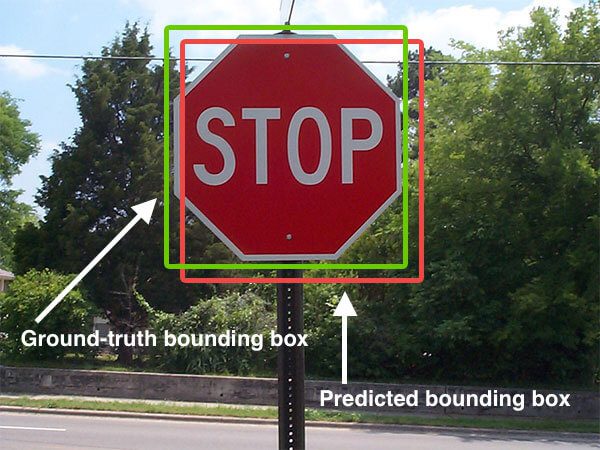 Intersection over Union (IoU) for object detection - PyImageSearch | Discover how to apply the Intersection over Union metric (Python code included) to evaluate custom object detectors.
Intersection over Union (IoU) for object detection - PyImageSearch | Discover how to apply the Intersection over Union metric (Python code included) to evaluate custom object detectors. How Compute Accuracy For Object Detection works—ArcGIS Pro ... | In the image below, the red bounding boxes indicate a positive ... The IoU ratio equals the overlap of bounding boxes (1) over the union of The ...
How Compute Accuracy For Object Detection works—ArcGIS Pro ... | In the image below, the red bounding boxes indicate a positive ... The IoU ratio equals the overlap of bounding boxes (1) over the union of The ... Metrics Matter: A Deep Dive into Object Detection Evaluation | by ... | In the ever-evolving field of computer vision, accurate evaluation metrics are essential for assessing the capabilities of models designed…
Metrics Matter: A Deep Dive into Object Detection Evaluation | by ... | In the ever-evolving field of computer vision, accurate evaluation metrics are essential for assessing the capabilities of models designed… YOLO Performance Metrics - Ultralytics YOLO Docs | Explore essential YOLO11 performance metrics like mAP, IoU, F1 Score, Precision, and Recall. Learn how to calculate and interpret them for model evaluation.
YOLO Performance Metrics - Ultralytics YOLO Docs | Explore essential YOLO11 performance metrics like mAP, IoU, F1 Score, Precision, and Recall. Learn how to calculate and interpret them for model evaluation.