Update npm Packages to Latest Versions
Learn how to efficiently check for outdated npm packages in your project and update them seamlessly to ensure optimal performance and security.
Learn how to efficiently check for outdated npm packages in your project and update them seamlessly to ensure optimal performance and security.
Staying current with your project's dependencies is crucial for maintaining security, performance, and access to the latest features. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to effectively managing your npm packages, ensuring your project remains healthy and up-to-date. We'll explore methods for identifying outdated packages, updating them safely, and understanding the role of the package-lock.json file. Additionally, we'll delve into best practices for maintaining your dependencies and introduce helpful tools to streamline the process.
Here's a comprehensive guide to checking and updating your npm packages, incorporating insights from the provided resources:
1. Identifying Outdated Packages:
There are two primary methods to check for outdated packages:
npm outdated: This command lists all dependencies in your package.json along with their current, wanted, and latest versions. It provides a clear overview of which packages need updates.npm outdatednpm-check-updates: This is a more powerful tool that not only lists outdated packages but also allows you to interactively choose which ones to update.
a. Installation:
npm install -g npm-check-updatesb. Usage:
ncu // Lists outdated packages
ncu -u // Updates package.json with latest versions2. Updating Packages:
Once you've identified outdated packages, you have several options for updating them:
npm update: This command updates packages to their latest versions within the version range specified in your package.json. It's a safe option as it avoids major version changes that could introduce breaking changes.npm updatenpm install <package-name>@latest: This command updates a specific package to its latest version, regardless of the version range in your package.json. Use this with caution as it might introduce breaking changes.npm install lodash@latestnpm-check-updates: After using ncu to list outdated packages and potentially update your package.json with ncu -u, you can run npm install to install the updated versions.3. Understanding package-lock.json:
package-lock.json file ensures consistent installations across different environments by locking down the exact versions of dependencies and sub-dependencies.package-lock.json file is automatically updated to reflect the new versions.package.json and package-lock.json to your version control system to maintain consistency.4. Best Practices:
5. Additional Tools:
By following these steps and best practices, you can keep your npm packages up-to-date, ensuring your project benefits from the latest features, bug fixes, and security improvements.
This code provides examples of how to keep NPM packages up-to-date using JavaScript. It shows how to check for outdated packages using both 'npm outdated' and 'npm-check-updates', and how to update packages using 'npm update' and 'npm install'. It also emphasizes the importance of understanding the 'package-lock.json' file and suggests best practices for managing package updates, such as regular checks, reviewing release notes, and testing. Additionally, it mentions tools like Version Lens and Dependabot that can further assist in the process.
While the provided guide explains the concepts well, let's illustrate them with practical JavaScript examples.
Note: These examples assume you have Node.js and npm installed.
1. Checking for Outdated Packages:
const { exec } = require('child_process');
// Using npm outdated
exec('npm outdated', (error, stdout, stderr) => {
if (error) {
console.error(`Error checking outdated packages: ${error}`);
return;
}
console.log(stdout); // Output the list of outdated packages
});
// Using npm-check-updates (requires prior installation: npm install -g npm-check-updates)
exec('ncu', (error, stdout, stderr) => {
if (error) {
console.error(`Error checking outdated packages: ${error}`);
return;
}
console.log(stdout); // Output the list of outdated packages
});2. Updating Packages:
const { exec } = require('child_process');
// Updating all packages within their specified range
exec('npm update', (error, stdout, stderr) => {
// Handle potential errors and output
});
// Updating a specific package to the latest version
const packageName = 'lodash';
exec(`npm install ${packageName}@latest`, (error, stdout, stderr) => {
// Handle potential errors and output
});3. Understanding package-lock.json:
While we cannot directly manipulate package-lock.json with JavaScript, it's crucial to understand its role. After running npm install or updating packages, inspect the changes in package-lock.json to see how specific versions are locked down.
4. Best Practices:
package.json, to run them periodically.axios or the native https module to fetch and parse release notes from package repositories before updating.5. Additional Tools (Integration Examples):
Remember: These examples provide a basic framework. You'll need to adapt and expand them based on your specific project requirements and workflow.
npm audit to identify and fix known security issues in your dependencies.npm ls can help you visualize your dependency tree and identify potential conflicts. You may need to manually resolve conflicts by adjusting version constraints or finding alternative packages.package-lock.json or yarn.lock, to ensure consistent installations across environments.Remember, keeping your npm packages up-to-date is an ongoing process. By incorporating these additional notes and best practices into your workflow, you can ensure the long-term health, security, and stability of your projects.
| Step | Command/Tool | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Identify Outdated Packages | npm outdated |
Lists outdated packages with current, wanted, and latest versions. |
npm-check-updates (ncu) |
More powerful tool to list and interactively update packages. | |
| Update Packages | npm update |
Updates packages to latest versions within specified range in package.json. |
npm install <package-name>@latest |
Updates a specific package to its latest version (use with caution). | |
npm-check-updates (ncu) |
Updates package.json and installs updated versions. |
|
Understand package-lock.json |
Locks down exact dependency versions for consistent installations. | |
| Best Practices | Regularly check for updates, review release notes, test thoroughly, consider semantic versioning. | |
| Additional Tools | Version Lens (VS Code) | Visual indicator of outdated packages. |
| Dependabot (GitHub) | Automates dependency updates through pull requests. |
By diligently following these guidelines and integrating them into your development workflow, you can ensure that your projects remain secure, performant, and equipped with the latest features. Remember, keeping your npm packages up-to-date is an ongoing commitment, but the benefits of doing so are undeniable. By embracing these practices, you contribute to the overall health and sustainability of your projects, fostering a more robust and reliable development ecosystem.
 npm-check-updates - npm | Find newer versions of dependencies than what your package.json allows. Latest version: 16.14.18, last published: a month ago. Start using npm-check-updates in your project by running
npm-check-updates - npm | Find newer versions of dependencies than what your package.json allows. Latest version: 16.14.18, last published: a month ago. Start using npm-check-updates in your project by running npm i npm-check-updates. There are 550 other projects in the npm registry using npm-check-updates. How to Update NPM Dependencies | The Node Package Manager (npm) provides various features to help you install and maintain your project's dependencies. Dependencies can become outdated over time due to bug fixes, new features, and other updates. The more project dependencies you have, the harder it is to keep up with these updates. Outdated
How to Update NPM Dependencies | The Node Package Manager (npm) provides various features to help you install and maintain your project's dependencies. Dependencies can become outdated over time due to bug fixes, new features, and other updates. The more project dependencies you have, the harder it is to keep up with these updates. Outdated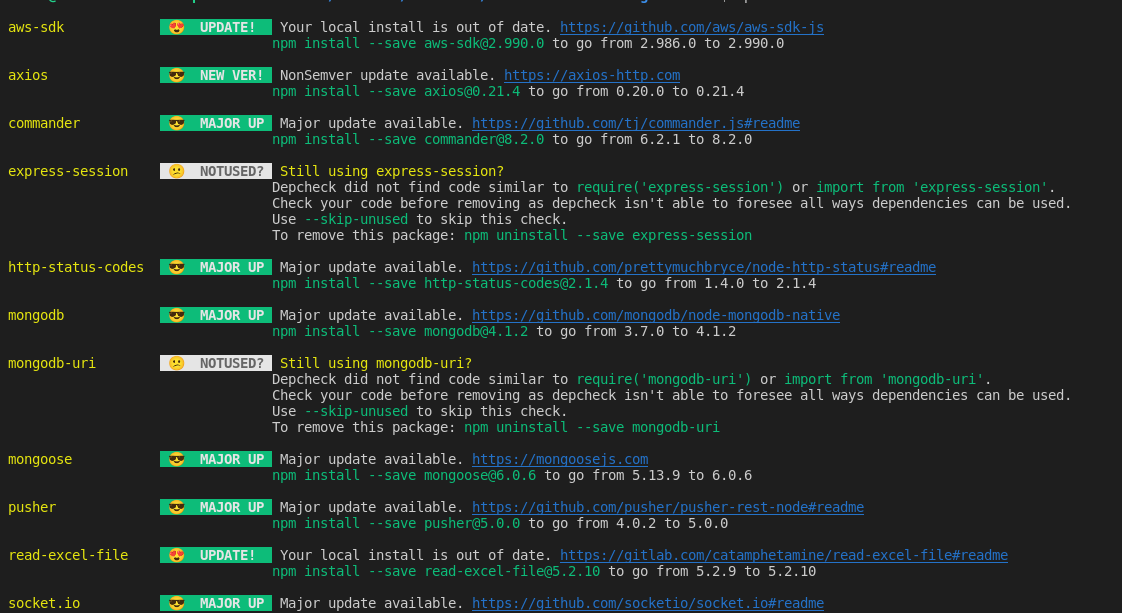 How to check and update npm packages | by Lizen Shakya | Medium | In our application, we use different npm packages. We need to update the packages from time to time as new versions of packages will be…
How to check and update npm packages | by Lizen Shakya | Medium | In our application, we use different npm packages. We need to update the packages from time to time as new versions of packages will be… How to Update Npm Packages Safely With Npm Check Updates | When you come back to an old web dev project, it’s important to update your packages to get new features, bug fixes, and security patches. NPM Check Updates is a CLI that will help you safely make those updates.
How to Update Npm Packages Safely With Npm Check Updates | When you come back to an old web dev project, it’s important to update your packages to get new features, bug fixes, and security patches. NPM Check Updates is a CLI that will help you safely make those updates. Run npm outdated to check old packages - DEV Community | There are things we might skip while learning web development from scratch. Knowing the ins and...
Run npm outdated to check old packages - DEV Community | There are things we might skip while learning web development from scratch. Knowing the ins and...npm update --save · Issue #3417 · npm/npm · GitHub | To update outdated packages + change the package.json accordingly, currently this is the workflow: Run npm outdated to figure out what needs to be updated. Then, for each package, run install with ...