Uninstall Node.js Windows Guide
Learn how to completely uninstall Node.js and npm from your Windows system, including removing leftover files and environment variables, for a clean slate.
Learn how to completely uninstall Node.js and npm from your Windows system, including removing leftover files and environment variables, for a clean slate.
This guide provides a comprehensive walkthrough on how to completely uninstall Node.js and npm from your Windows system. It covers using the Control Panel, clearing the npm cache, manually deleting leftover files, checking environment variables, and restarting your computer. Additional notes address using package managers and troubleshooting potential issues.
Here's how to completely remove Node.js and npm from your Windows system:
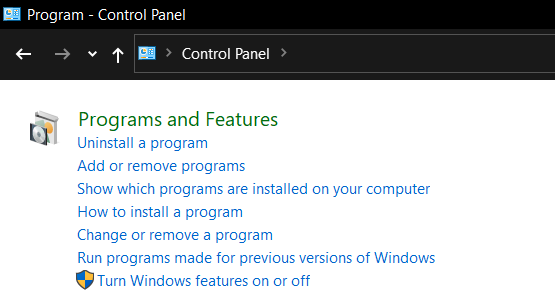
1. Uninstall via Control Panel:
2. Clear npm cache:
Even after uninstalling, some leftover files might remain. Let's clear the npm cache:
npm cache clean --forceThis command forcefully clears the npm cache, removing any remaining packages or data.
3. Manually delete remaining files (Optional):
For a thorough cleanup, you can manually delete the following directories:
Note: Replace [Your Username] with your actual Windows username.
4. Check environment variables (Optional):
5. Restart your computer:
After completing the above steps, restart your computer to ensure all changes take effect.
Additional Notes:
choco uninstall nodejs).By following these steps, you should have successfully removed Node.js and npm from your Windows system. You can now proceed with a fresh installation or explore other development tools.
This code snippet demonstrates how to use JavaScript in conjunction with Node Version Manager (nvm) to manage multiple Node.js versions on a system. While not directly uninstalling Node.js, it provides a way to switch between different versions, achieving a similar outcome. The code defines functions to execute shell commands and switch between Node.js versions using nvm. This allows for flexibility in development environments where different projects may require specific Node.js versions.
While the provided instructions are for manual uninstallation steps on Windows, there's no direct JavaScript code involved in the process. Uninstalling software like Node.js typically involves system-level operations and interacting with the Windows Control Panel or package managers.
However, let's explore how you might use JavaScript to achieve similar results in a different context:
Scenario: Managing Node.js versions with nvm (Node Version Manager)
nvm is a popular tool for managing multiple Node.js versions on a single machine. Here's how you can use JavaScript along with nvm to switch between Node.js versions, which indirectly achieves a similar outcome to uninstalling and reinstalling:
const { exec } = require('child_process');
// Function to execute shell commands
function runCommand(command) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
exec(command, (error, stdout, stderr) => {
if (error) {
reject(error);
} else {
resolve(stdout.trim());
}
});
});
}
// Example usage:
async function switchNodeVersion(version) {
try {
// Check if the version is installed
const installedVersions = await runCommand('nvm ls');
if (!installedVersions.includes(version)) {
console.log(`Installing Node.js version ${version}`);
await runCommand(`nvm install ${version}`);
}
// Use the specified version
console.log(`Using Node.js version ${version}`);
await runCommand(`nvm use ${version}`);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error:', error);
}
}
// Example: Switch to Node.js version 14.18.0
switchNodeVersion('14.18.0');Explanation:
exec: We import the exec function from the child_process module to execute shell commands.runCommand Function: This helper function executes a given shell command and returns a Promise that resolves with the command's output.switchNodeVersion Function:
nvm ls.nvm install to install the version.nvm use to switch to the specified version.Remember: This example requires having nvm installed and configured on your system.
Limitations:
npm list -g --depth=0. This can help you decide whether to reinstall them later.| Step | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Uninstall via Control Panel | Remove Node.js using the Programs and Features (or Add/Remove Programs) option. |
| 2 | Clear npm cache | Use the command npm cache clean --force in a terminal to remove leftover npm data. |
| 3 | Manually delete remaining files (Optional) | Delete directories associated with Node.js and npm, including C:\Program Files\nodejs, C:\Users\[Your Username]\AppData\Roaming\npm, and C:\Users\[Your Username]\AppData\Roaming\npm-cache. |
| 4 | Check environment variables (Optional) | Remove any Node.js or npm related entries from the System variables under Environment Variables. |
| 5 | Restart your computer | Reboot the system to ensure all changes take effect. |
By following the outlined steps, you can effectively remove Node.js and npm from your Windows system. This process involves using the Control Panel, clearing the npm cache, manually deleting remaining files (optional), checking environment variables (optional), and restarting your computer. Remember to consider additional factors such as global packages, project dependencies, registry configurations, third-party tools, and data backups to ensure a smooth uninstallation process. Whether you're preparing for a fresh installation or exploring alternative development tools, these instructions provide a clear roadmap for successfully uninstalling Node.js and npm from your Windows environment.
 How to completely remove node.js from Windows ? - GeeksforGeeks | A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.
How to completely remove node.js from Windows ? - GeeksforGeeks | A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions. How to uninstall Node.js? Remove Node.js from your system ... | There is no restriction on the type of programming language used for writing server-side code. Some of the popular examples include PHP, Ruby, C#, Python, and Javascript. Out of all these, Javascript is very much popular because of its beginner-friendliness and being able to be used both on the client-side and server-side as well. As
How to uninstall Node.js? Remove Node.js from your system ... | There is no restriction on the type of programming language used for writing server-side code. Some of the popular examples include PHP, Ruby, C#, Python, and Javascript. Out of all these, Javascript is very much popular because of its beginner-friendliness and being able to be used both on the client-side and server-side as well. As How to completely remove node js from Windows | Edureka ... | I removed my prior version of node.js (0.8.11), then downloaded and installed the current version, 0.10 ... . I'm using a 64-bit version of Windows 7.
How to completely remove node js from Windows | Edureka ... | I removed my prior version of node.js (0.8.11), then downloaded and installed the current version, 0.10 ... . I'm using a 64-bit version of Windows 7. Sharepoint development framework environment setup. Yeoman ... | Following the guide https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sharepoint/dev/spfx/set-up-your-development-environmentmade sure of all the prerequisites but as I follow..
Sharepoint development framework environment setup. Yeoman ... | Following the guide https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sharepoint/dev/spfx/set-up-your-development-environmentmade sure of all the prerequisites but as I follow..