Terraform Route 53 Record to ALB Configuration
Learn how to use Terraform to effortlessly create a Route 53 record that directs traffic to your Application Load Balancer (ALB) in AWS.
Learn how to use Terraform to effortlessly create a Route 53 record that directs traffic to your Application Load Balancer (ALB) in AWS.
This guide explains how to connect your domain name to an Application Load Balancer (ALB) in AWS using Route 53. Before you begin, ensure you have a registered domain name in Route 53 and an ALB configured in your AWS account. You'll need your domain name and the ALB's DNS name, which you can find in the ALB details within the EC2 console. To create the connection, you'll set up an ALIAS record in Route 53. This involves using Terraform's aws_route53_record resource, specifying 'A' as the record type and configuring the 'alias' block with your ALB's DNS name and your Route 53 hosted zone ID. Once you've saved your Terraform configuration, run 'terraform apply' to create the record. Remember that ALIAS records are the correct choice for ALBs, not CNAME records. Also, ensure your ALB has properly configured listeners and targets for health checks. After the changes are applied, allow time for DNS propagation. If you encounter issues, verify your ALB's DNS name, zone ID, and the ALB's health status. For Terraform errors, review the messages for syntax problems or permission issues.
To connect your domain name to an Application Load Balancer (ALB) using Route 53, you'll need to create an ALIAS record. Here's a breakdown:
Prerequisites:
Gather Information:
example.com).your-alb-name-1234567890.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com.Create the ALIAS Record:
aws_route53_record resource with type = "A" and alias block.
name to your desired subdomain (e.g., blog for blog.example.com or leave empty for the root domain).alias block:
name should point to your ALB's DNS name.zone_id is the Route 53 hosted zone ID where your domain is managed.evaluate_target_health should generally be set to true for ALBs.Apply Changes:
terraform apply to create the record in Route 53.Important Considerations:
name attribute in aws_route53_record determines the subdomain. An empty string represents the root domain.Troubleshooting:
This Terraform code configures an AWS Route 53 ALIAS record to point your root domain name to an Application Load Balancer (ALB). It uses variables for flexibility and includes health check configuration. You need to provide your domain name, ALB DNS name, and hosted zone ID.
# Configure the AWS Provider
terraform {
required_providers {
aws = {
source = "hashicorp/aws"
version = "~> 4.0" # Use the latest version compatible with your setup
}
}
}
# Variables (Replace with your actual values)
variable "domain_name" {
default = "example.com"
}
variable "alb_dns_name" {
default = "your-alb-name-1234567890.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com"
}
variable "hosted_zone_id" {
# Get this from the Route 53 console
default = "YOUR_HOSTED_ZONE_ID"
}
# Create an ALIAS record for the root domain
resource "aws_route53_record" "alb_record" {
zone_id = var.hosted_zone_id
name = var.domain_name
type = "A"
alias {
name = var.alb_dns_name
zone_id = var.hosted_zone_id # Use the same hosted zone ID
evaluate_target_health = true
}
}Explanation:
aws_route53_record Resource: This resource defines a new Route 53 record.
zone_id: Specifies the Route 53 hosted zone where the record will be created.name: Sets the subdomain. In this case, it's an empty string ("") to target the root domain (example.com).type: Set to "A" for an address record.alias: Configures the record as an ALIAS record.
name: The ALB's DNS name.zone_id: The hosted zone ID of the ALB (which is the same as your domain's hosted zone ID).evaluate_target_health: Enables Route 53 health checks on the ALB.How to Use:
terraform init
terraform apply
Additional Notes:
blog.example.com), set the name attribute to the desired subdomain ("blog" in this case).aws_route53_record resources to define records for different subdomains or purposes.terraform destroy.aws_route53_record data source and then modify it to be an ALIAS record.This guide outlines how to connect your domain name to an Application Load Balancer (ALB) using an ALIAS record in Route 53.
Before You Begin:
Steps:
Gather Information:
example.com).your-alb-name-1234567890.us-east-1.elb.amazonaws.com).Create the ALIAS Record (using Terraform):
aws_route53_record resource with type = "A" and the alias block.name attribute to your desired subdomain (e.g., blog for blog.example.com) or leave it empty for the root domain.alias block:
name to your ALB's DNS name.zone_id to the Route 53 hosted zone ID where your domain is managed.evaluate_target_health to true for ALBs.Apply Changes:
terraform apply to create the record in Route 53.Key Points:
Troubleshooting:
By following these steps, you can effectively connect your domain name to an Application Load Balancer using Route 53, ensuring traffic is routed efficiently and reliably to your applications. Remember to leverage Terraform for streamlined infrastructure management and refer to the provided code example for a practical starting point. Always consult the AWS documentation for the latest features, updates, and best practices.
brand.com) as an ALIAS record - cloudposse/terraform-aws-route53-alias Resource changes during destroy - Terraform - HashiCorp Discuss | Hi, Let say I have route53 service in AWS redirected into some ip address. I run terraform which redirects route53 into ALB created by that terraform. If I run apply - everything works and route53 redirects into newly created ALB. Then this record is destroyed if run terraform destroy command. Can I restore previous value of record during destroy or run “aws_route53_record” to create new record during destroy command? Thanks, Dmitriy
Resource changes during destroy - Terraform - HashiCorp Discuss | Hi, Let say I have route53 service in AWS redirected into some ip address. I run terraform which redirects route53 into ALB created by that terraform. If I run apply - everything works and route53 redirects into newly created ALB. Then this record is destroyed if run terraform destroy command. Can I restore previous value of record during destroy or run “aws_route53_record” to create new record during destroy command? Thanks, Dmitriy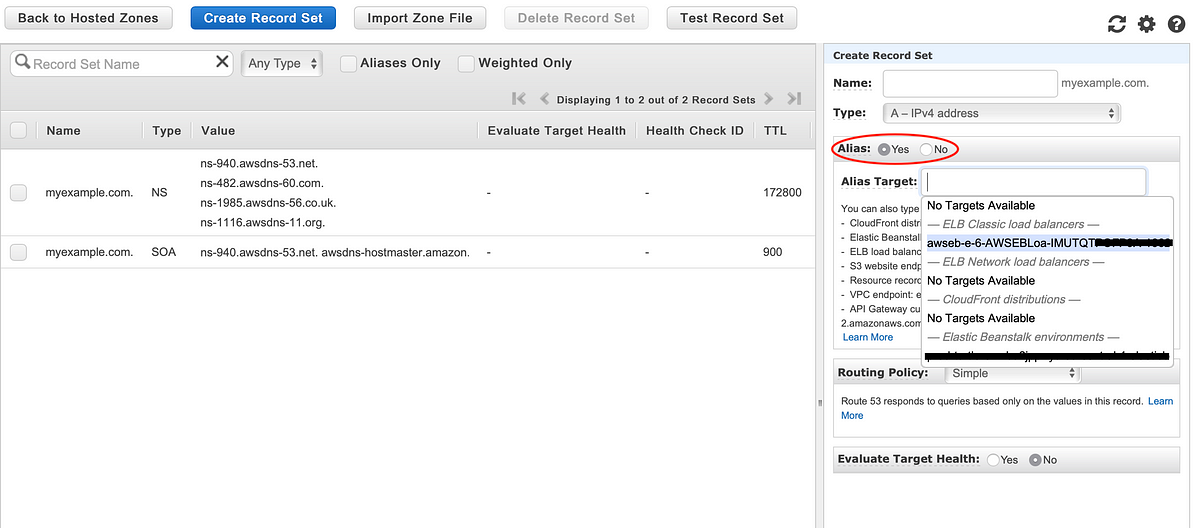 AWS + Terraform: Elastic Beanstalk alias in Route 53 | by Flo Sloot ... | Jeez, actually took me some time to figure out how to create an ALIAS DNS-record for an elastic beanstalk environment in Terraform.
AWS + Terraform: Elastic Beanstalk alias in Route 53 | by Flo Sloot ... | Jeez, actually took me some time to figure out how to create an ALIAS DNS-record for an elastic beanstalk environment in Terraform.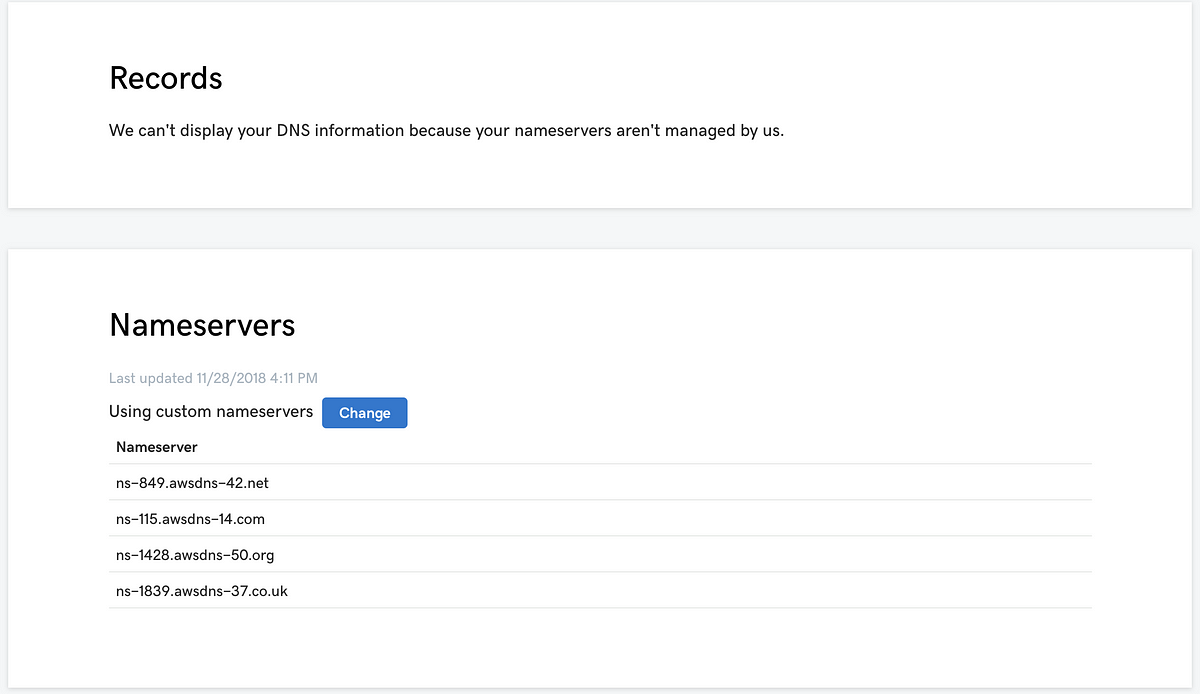 Domain by GoDaddy, DNS by Route53 | by Ryan Canty | Medium | Just because GoDaddy registered your domain doesn’t mean they have to manage your DNS.
Domain by GoDaddy, DNS by Route53 | by Ryan Canty | Medium | Just because GoDaddy registered your domain doesn’t mean they have to manage your DNS.