PHP Error Log Location: Where to Find It
Learn how to locate and troubleshoot errors in your PHP applications by understanding where PHP stores its error log files.
Learn how to locate and troubleshoot errors in your PHP applications by understanding where PHP stores its error log files.
Finding PHP error logs can be a bit like a scavenger hunt, as their location isn't always obvious and depends on your specific setup. This guide will walk you through the common places to look for these logs, helping you troubleshoot issues effectively.
PHP error logs can be tricky to find because their location depends on your setup. Here's a breakdown:
1. Check your PHP configuration:
The error_log directive in your php.ini file dictates where errors are logged.
error_log = /path/to/your/error.log2. Common locations:
/xampp/apache/logs/error.log
/var/log/apache2/error.log (if using Apache)3. Web server logs:
If PHP errors aren't in the PHP error log, check your web server's logs:
/var/log/apache2/error.log
/var/log/nginx/error.log
4. PHP-FPM:
If using PHP-FPM, the log location is defined in the php-fpm.conf file, usually within the catch_workers_output directive.
5. Custom locations:
You can set a custom log file path in your PHP script using ini_set():
ini_set('error_log', '/my/custom/path/error.log');6. Enable error display:
For development, enable error display in your php.ini:
display_errors = On7. Error logging levels:
Control which errors are logged with error_reporting:
error_reporting(E_ALL); // Log all errors8. Use error monitoring tools:
Tools like Rollbar can centralize error logs and provide more detailed debugging information.
This code provides examples of how to find and configure PHP error logs, including finding the php.ini file, setting a custom error log path, checking the error log location in PHP-FPM, enabling error display for development, and using an error monitoring tool like Rollbar.
This code example demonstrates different ways to find and configure PHP error logs.
1. Finding the php.ini file:
<?php
$iniPath = php_ini_loaded_file();
echo "Loaded php.ini file: " . $iniPath;
?>2. Setting a custom error log path:
<?php
// Set custom error log path
ini_set('error_log', '/my/custom/path/error.log');
// Trigger an error
trigger_error("This is a custom error message", E_USER_WARNING);
?>3. Checking error log location in PHP-FPM:
# Assuming php-fpm.conf is located at /etc/php/7.4/fpm/php-fpm.conf
grep catch_workers_output /etc/php/7.4/fpm/php-fpm.conf4. Enabling error display for development:
Note: This is not recommended for production environments.
<?php
ini_set('display_errors', 1);
ini_set('display_startup_errors', 1);
error_reporting(E_ALL);
// Trigger an error
echo $undefinedVariable;
?>5. Using error monitoring tools (example with Rollbar):
<?php
// Include the Rollbar library
require_once 'path/to/vendor/autoload.php';
// Configure Rollbar
Rollbar\Rollbar::init([
'access_token' => 'YOUR_ROLLBAR_ACCESS_TOKEN',
'environment' => 'production'
]);
// Report an error to Rollbar
try {
// Code that might throw an exception
} catch (Exception $e) {
Rollbar\Rollbar::error($e);
}
?>This code provides examples for:
php.ini file.Remember to adapt these examples to your specific environment and needs.
Best Practices for PHP Error Logging
Troubleshooting Common Error Log Issues
Security Considerations
Alternatives to Traditional Error Logs
PHP error log locations vary depending on your server setup. Here's a breakdown:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
PHP Configuration (php.ini) |
The error_log directive defines the log file path. |
| Common Server Locations | - XAMPP: /xampp/apache/logs/error.log - Debian/Ubuntu (Apache): /var/log/apache2/error.log - cPanel: Check your cPanel error log settings. |
| Web Server Logs | If not in the PHP log, check: - Apache: /var/log/apache2/error.log - Nginx: /var/log/nginx/error.log
|
| PHP-FPM | The php-fpm.conf file, usually the catch_workers_output directive, defines the log location. |
| Custom Locations | Use ini_set('error_log', '/your/custom/path/error.log'); in your script. |
Additional Tips:
display_errors = On in php.ini for development.error_reporting(E_ALL); to log all errors.Mastering PHP error logs is crucial for efficient debugging and maintaining a healthy application. While their location can be elusive, understanding your server setup and PHP configuration is key. Remember to prioritize security by disabling error display in production and protecting your log files. For enhanced error management, explore dedicated error monitoring services and logging frameworks. By effectively utilizing these strategies, you can transform PHP error logs from cryptic messages into valuable tools for building robust and reliable applications.
 Where can I find error log files for PHP? | Better Stack Community | Ship higher-quality software faster. Be the hero of your engineering teams.
Where can I find error log files for PHP? | Better Stack Community | Ship higher-quality software faster. Be the hero of your engineering teams. Where are PHP Errors Logged? | Rollbar | This simple guide explains where PHP logs are located, how to configure logging, and why error monitoring tools like Rollbar make debugging even faster.
Where are PHP Errors Logged? | Rollbar | This simple guide explains where PHP logs are located, how to configure logging, and why error monitoring tools like Rollbar make debugging even faster.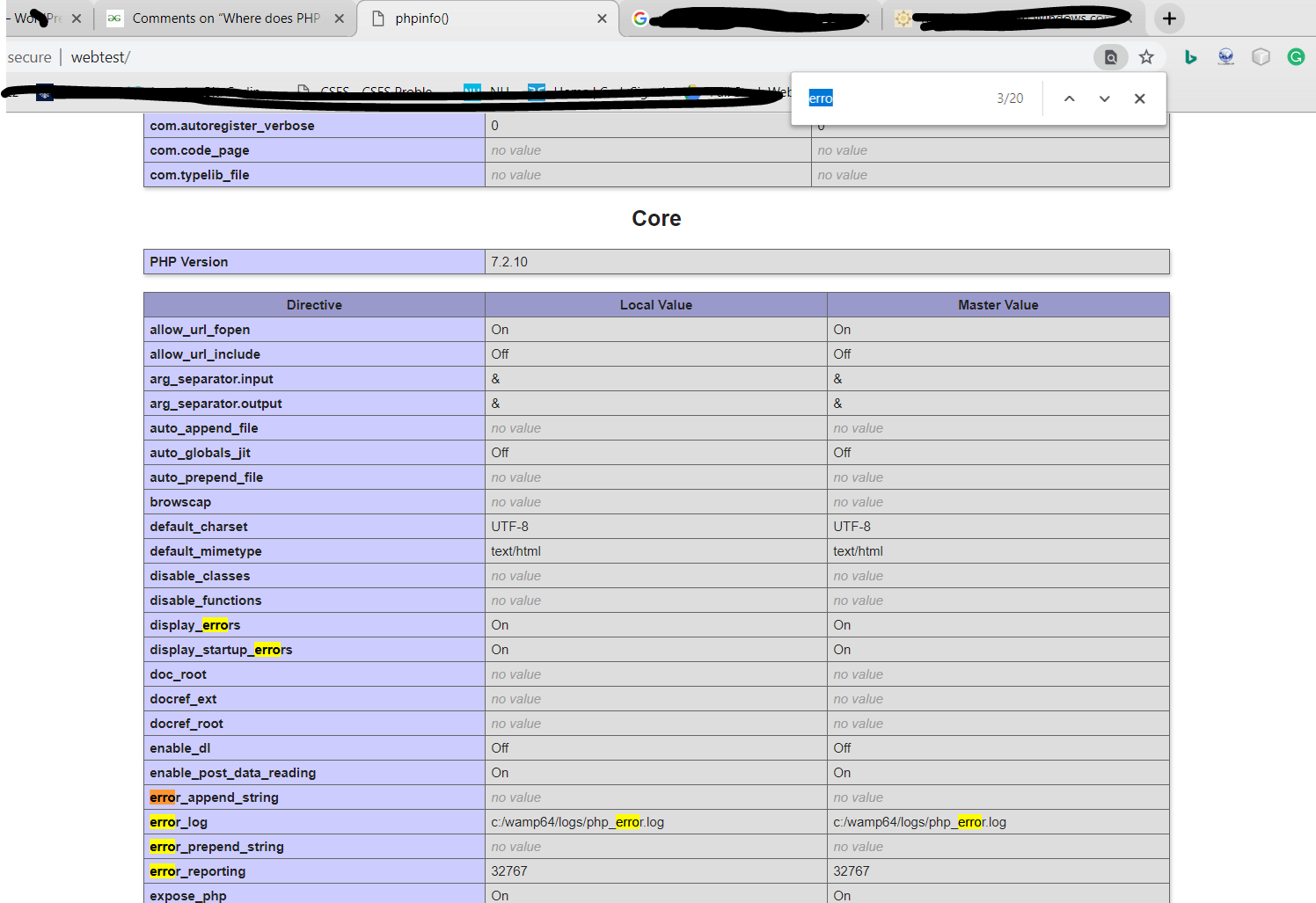 Where does PHP store the error log? (php5, apache, fastcgi, cpanel ... | A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.
Where does PHP store the error log? (php5, apache, fastcgi, cpanel ... | A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions. PHP error logs - MoodleDocs | May 1, 2024 ... The location of the error log file itself can be set manually in the php.ini file. On a Windows server, in IIS, it may be something like "' ...
PHP error logs - MoodleDocs | May 1, 2024 ... The location of the error log file itself can be set manually in the php.ini file. On a Windows server, in IIS, it may be something like "' ... Solved - Please help to send php-fpm error logs to nginx error logs ... | Greetings,
Solved - Please help to send php-fpm error logs to nginx error logs ... | Greetings,This is what I've been struggling with for a while now. I was wondering maybe somebody has experience with this.
So I have php 8.1.23 and nginx 1.24.0 installed from ports. Then I use php-fpm as fastcgi service to communicate with nginx.
Everything works perfectly, but errors...
 How to Automate PHP Error Logging Quickly | Learn how to automate PHP error logging in web applications and resolve run-time exceptions to get optimized performance results.
How to Automate PHP Error Logging Quickly | Learn how to automate PHP error logging in web applications and resolve run-time exceptions to get optimized performance results.