PHP Static Code Analysis: Tools and Best Practices
Learn how to improve code quality and reduce bugs in your PHP projects with static code analysis tools and techniques.
Learn how to improve code quality and reduce bugs in your PHP projects with static code analysis tools and techniques.
Writing clean, error-free PHP code is crucial for any successful project. Static analysis tools are your allies in this endeavor, helping you catch potential problems early in the development process. This article guides you through implementing static analysis in your PHP workflow, from basic syntax checks to advanced analysis with popular tools like PHPStan, Psalm, and PHPMD.
Start with PHP's built-in linter:
php -l your_script.phpThis checks for basic syntax errors.
Choose a static analysis tool: Popular options include:
composer require --dev phpstan/phpstan
./vendor/bin/phpstan analyse srccomposer require --dev vimeo/psalm
./vendor/bin/psalmcomposer require --dev phpmd/phpmd
./vendor/bin/phpmd src text controversialIntegrate into your workflow:
Configure the tool:
Address the findings:
Iterate and improve:
This code snippet demonstrates how to use various PHP static analysis tools like PHP's built-in linter, PHPStan, Psalm, and PHPMD to identify potential issues in your code. It provides examples of running each tool against a PHP file containing intentional errors, such as an undefined variable and a type mismatch. The description explains that these tools can be integrated into local development workflows or CI/CD pipelines to automate code quality checks. It emphasizes the importance of configuration, starting with less strict rules and gradually increasing the strictness, and iteratively addressing the findings to improve code quality over time.
<?php
// filename: example.php
// Example of a potential issue: undefined variable
function greet($name) {
echo "Hello, $namee!"; // Typo in variable name
}
// Example of a type mismatch:
function add(int $a, int $b): int {
return $a . $b; // Incorrect concatenation instead of addition
}
greet("Alice");
echo add(5, 10);
?>1. Using PHP's built-in linter:
php -l example.php2. Using PHPStan:
composer require --dev phpstan/phpstan
# Create a phpstan.neon configuration file (optional but recommended)
# Example content for phpstan.neon:
# parameters:
# level: 5
./vendor/bin/phpstan analyse example.php3. Using Psalm:
composer require --dev vimeo/psalm
./vendor/bin/psalm --show-info=false example.php4. Using PHPMD:
composer require --dev phpmd/phpmd
./vendor/bin/phpmd example.php text controversialExplanation:
example.php file contains intentional errors to demonstrate the tools.$name parameter in the greet function.Integrating into your workflow:
Configuration and Iteration:
Understanding the tools: While all three tools (PHPStan, Psalm, PHPMD) aim to improve code quality, they have different strengths:
Gradual adoption: Don't feel overwhelmed by the potential findings. Start with a basic configuration and gradually increase the strictness as you become more comfortable.
False positives: Static analysis tools aren't perfect. They might flag code that's technically correct but written in an unusual way. Use your judgment to determine if a finding is a genuine issue or a false positive.
Beyond the basics: Explore additional features offered by these tools:
Benefits beyond bug catching: Static analysis not only helps prevent bugs but also:
Continuous improvement: Static analysis is an ongoing process. Regularly review the findings, adjust the configuration, and strive to write cleaner and more robust PHP code.
This article provides a concise guide to implementing static analysis in your PHP projects:
1. Basic Syntax Check:
php -l your_script.php) to catch syntax errors.2. Choose a Static Analysis Tool:
3. Integrate into Workflow:
4. Configure the Tool:
5. Address Findings:
6. Iterate and Improve:
By embracing static analysis as an integral part of your PHP development process, you can significantly enhance code quality, reduce bugs, and build more robust applications. Remember to start with the basics, gradually increase the strictness of your analysis, and continuously iterate based on the findings. With the help of powerful tools like PHPStan, Psalm, and PHPMD, you can elevate your codebase and strive for excellence in your PHP projects.
 Keep your code under control with PHP static code analysis tools | Keeping code clean is not easy. That’s why in this article, I present some useful tools which can help you with PHP static code analysis. Learn more.
Keep your code under control with PHP static code analysis tools | Keeping code clean is not easy. That’s why in this article, I present some useful tools which can help you with PHP static code analysis. Learn more. Psalm - a static analysis tool for PHP | Psalm is a free & open-source static analysis tool that helps you identify problems in your code, so you can sleep a little better.
Psalm - a static analysis tool for PHP | Psalm is a free & open-source static analysis tool that helps you identify problems in your code, so you can sleep a little better. 5 Great PHP Code Analysis Tools Recommended by Developers ... | The developer community has a diverse ecosystem of static PHP code analysis tools which can make it somewhat difficult to decide which ones to use...
5 Great PHP Code Analysis Tools Recommended by Developers ... | The developer community has a diverse ecosystem of static PHP code analysis tools which can make it somewhat difficult to decide which ones to use...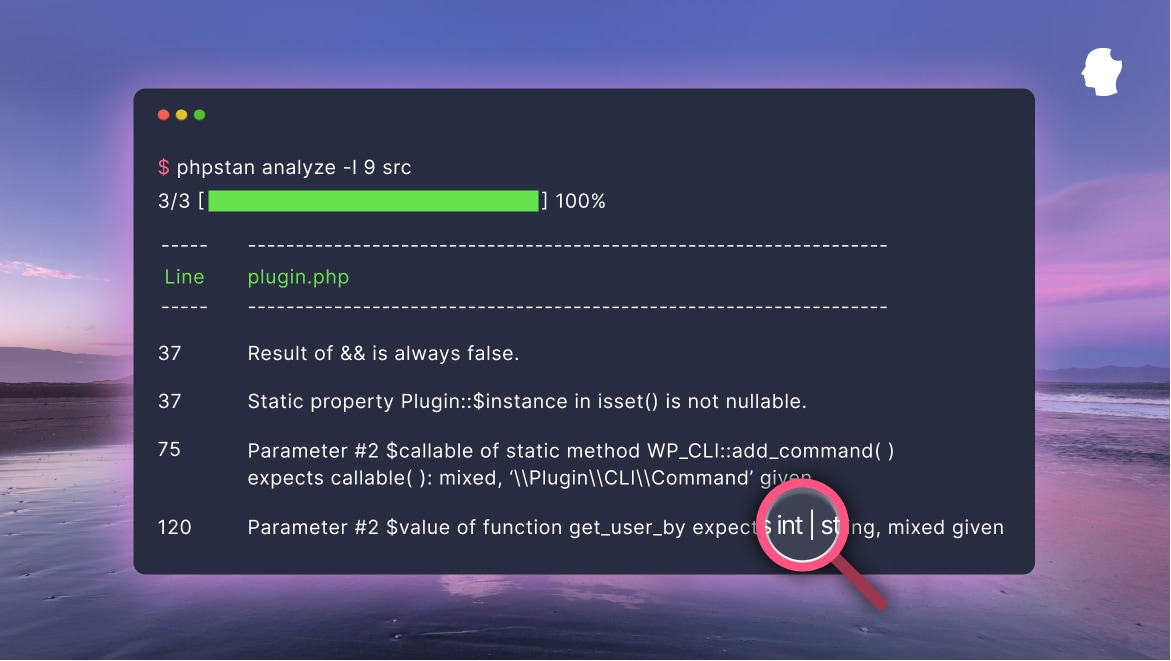 Get Started with PHP Static Code Analysis | Get started with our guide to PHP static code analysis tools and detect problems before you even run the code.
Get Started with PHP Static Code Analysis | Get started with our guide to PHP static code analysis tools and detect problems before you even run the code. Recommendation - Static code analysis - Katalon Studio - Katalon ... | Do you have any recommendation for a static code analysis tool or plugin to use with Katalon Studio ?
Recommendation - Static code analysis - Katalon Studio - Katalon ... | Do you have any recommendation for a static code analysis tool or plugin to use with Katalon Studio ?