PHP Array Storage: json_encode or serialize?
Explore the pros and cons of json_encode and serialize for storing PHP arrays, optimizing data storage and retrieval for your web applications.
Explore the pros and cons of json_encode and serialize for storing PHP arrays, optimizing data storage and retrieval for your web applications.
When working with PHP, efficiently storing and retrieving arrays is a common task. Two popular methods for achieving this are json_encode and serialize. Each offers unique advantages and understanding their strengths helps determine the best approach for your project.
Let's break down the best ways to store PHP arrays, focusing on json_encode and serialize.
Understanding the Core Concepts
Serialization (serialize): This PHP-specific function transforms any PHP data structure (like arrays or objects) into a string. This string can be stored and later reconstructed back into the original data structure using unserialize.
$my_array = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry'];
$serialized_data = serialize($my_array);
// $serialized_data now holds a string representation of the arrayJSON Encoding (json_encode): This method converts PHP data into a JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) string. JSON is a widely used, language-independent format for data exchange. You can reverse the process using json_decode to get back your PHP array or object.
$my_array = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry'];
$json_data = json_encode($my_array);
// $json_data contains a JSON string representing the arrayWhen to Choose What
Interoperability: If you need to share your data with applications written in other languages (JavaScript, Python, etc.), JSON is the way to go. It's the standard for data exchange across different systems.
PHP-Specific Storage: If you're only working within a PHP environment and need to store complex data structures (including objects with methods), serialize is a good choice.
Performance: In modern PHP versions, json_encode and json_decode are generally faster than serialize and unserialize.
Data Types: JSON has limitations on the data types it can represent directly. For instance, PHP resource types cannot be encoded in JSON.
Important Considerations
Database Storage: While you can store serialized or JSON-encoded data in a database, it's often not ideal for complex queries. Relational databases are designed for structured data.
Security: Be cautious when unserialize-ing data from untrusted sources. It can potentially lead to security vulnerabilities if the data is maliciously crafted.
In essence:
json_encode for its speed, readability, and compatibility with other programming languages.serialize when you need to store complex PHP data structures within a PHP-only environment.The code demonstrates two methods for storing and retrieving PHP arrays: serialization and JSON encoding. It first defines an example array, then uses serialize to convert it into a string and unserialize to restore the original array from the string. Next, it uses json_encode to convert the array into a JSON string and json_decode to decode it back into an array. The output shows the serialized string, the restored array, the JSON encoded string, and the decoded array, illustrating how both methods can be used to handle PHP arrays.
This code example demonstrates the use of json_encode and serialize for storing PHP arrays.
<?php
// Example array
$fruits = [
'name' => 'Fruit Basket',
'items' => ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry'],
'quantity' => 3
];
// Serialization
$serialized_fruits = serialize($fruits);
echo "Serialized Data:\n";
echo $serialized_fruits . "\n\n";
// Unserialization
$restored_fruits = unserialize($serialized_fruits);
echo "Restored Array (from Serialization):\n";
print_r($restored_fruits);
echo "\n\n";
// JSON Encoding
$json_fruits = json_encode($fruits);
echo "JSON Encoded Data:\n";
echo $json_fruits . "\n\n";
// JSON Decoding
$decoded_fruits = json_decode($json_fruits, true); // 'true' returns an associative array
echo "Decoded Array (from JSON):\n";
print_r($decoded_fruits);
?>Output:
Serialized Data:
a:3:{s:4:"name";s:12:"Fruit Basket";s:5:"items";a:3:{i:0;s:5:"apple";i:1;s:6:"banana";i:2;s:6:"cherry";}s:8:"quantity";i:3;}
Restored Array (from Serialization):
Array
(
[name] => Fruit Basket
[items] => Array
(
[0] => apple
[1] => banana
[2] => cherry
)
[quantity] => 3
)
JSON Encoded Data:
{"name":"Fruit Basket","items":["apple","banana","cherry"],"quantity":3}
Decoded Array (from JSON):
Array
(
[name] => Fruit Basket
[items] => Array
(
[0] => apple
[1] => banana
[2] => cherry
)
[quantity] => 3
)
Explanation:
$fruits.serialize to convert the array into a string representation.unserialize to reconstruct the original array from the serialized string.json_encode to convert the array into a JSON string.json_decode with the second parameter set to true to decode the JSON string back into an associative array.This example illustrates how both methods can be used to store and retrieve PHP arrays. Remember to choose the method that best suits your specific needs based on the factors discussed in the article.
serialize.json_encode and serialize can fail. Always check for errors using json_last_error() and unserialize()'s return value (which is false on failure) respectively.unserialize to prevent potential security risks.JSON_ENCODE() and JSON_DECODE() in MySQL).BLOB or TEXT column type.Choosing the right method depends on your specific needs. Carefully weigh the trade-offs between interoperability, performance, security, and data complexity to make an informed decision.
| Feature | json_encode |
serialize |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Converts PHP data to JSON string. | Converts PHP data to a PHP-specific string. |
| Output Format | JSON (language-independent) | PHP serialized string |
| Interoperability | Excellent (works with various languages) | Limited to PHP |
| Data Type Support | Limited (cannot handle PHP resources) | Extensive (handles complex PHP types) |
| Performance | Generally faster in modern PHP | Can be slower, especially with complex data |
| Security | Safer for untrusted data | Potential security risks with unserialize
|
| Ideal Use Case | Data exchange between different systems, web services | Storing complex PHP data within a PHP application |
Key Takeaways:
json_encode: Prioritize for speed, readability, and cross-language compatibility.serialize: Use for storing complex PHP data structures within a PHP-only environment.Important Notes:
unserialize with data from untrusted sources.By understanding the strengths of both json_encode and serialize, PHP developers can make informed decisions about how to best store and manage array data in their applications. json_encode emerges as the top choice for its speed, readability, and compatibility with other programming languages, making it ideal for data exchange and web services. On the other hand, serialize proves valuable when storing complex PHP data structures within a PHP-only environment. When making a choice, carefully consider factors like interoperability, performance, security, and data complexity to determine the most suitable approach for your specific project needs. Remember to prioritize security measures like data sanitization when using unserialize with data from untrusted sources. By selecting the appropriate method, developers can ensure efficient and reliable data handling in their PHP projects.
 Best practice...json_encode OR serialize? - PHP - SitePoint Forums ... | Am trying to store array information gathered from a form. The form is dynamic s the info can include a different number of fields and different names. As such it seems the best way to package the info is in an array or multidimensional array and then store that array into the DB. There seems to be two ways to do this: serialize() or json_encode() I was wondering which one is be considered the best practice. So for example the form could have any # of text inputs named detail/ paired w...
Best practice...json_encode OR serialize? - PHP - SitePoint Forums ... | Am trying to store array information gathered from a form. The form is dynamic s the info can include a different number of fields and different names. As such it seems the best way to package the info is in an array or multidimensional array and then store that array into the DB. There seems to be two ways to do this: serialize() or json_encode() I was wondering which one is be considered the best practice. So for example the form could have any # of text inputs named detail/ paired w...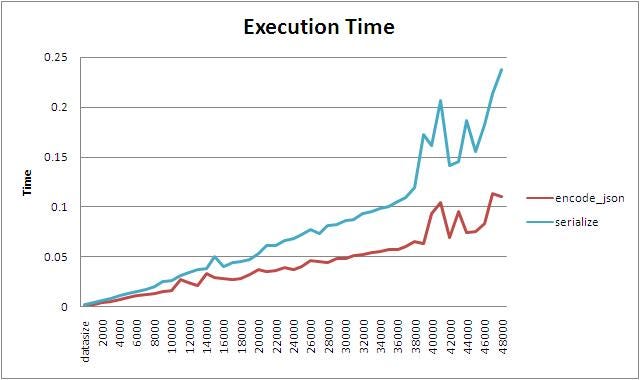 serialize vs json in PHP. Today I am discussing, serialize vs… | by ... | Today I am discussing, serialize vs json_encode and their opposite unserialize vs json_decode, maybe this topic allreay very simple to…
serialize vs json in PHP. Today I am discussing, serialize vs… | by ... | Today I am discussing, serialize vs json_encode and their opposite unserialize vs json_decode, maybe this topic allreay very simple to… SOLVED - Saving ds_grid using JSON | GameMaker Community | I'm doing some research right now on how to take my inventory system that uses a ds_grid and saving it properly using JSON (as I will be using cross platform eventually so not wanting to use ini). From what I've learned thus far is that I need to convert my ds_grid into a ds_map eventually to...
SOLVED - Saving ds_grid using JSON | GameMaker Community | I'm doing some research right now on how to take my inventory system that uses a ds_grid and saving it properly using JSON (as I will be using cross platform eventually so not wanting to use ini). From what I've learned thus far is that I need to convert my ds_grid into a ds_map eventually to...