Get Current URL in React: A Complete Guide
Learn how to easily access and utilize the current full URL within your React components for dynamic routing, data fetching, and more.
Learn how to easily access and utilize the current full URL within your React components for dynamic routing, data fetching, and more.
In React applications, retrieving the current URL is a common task, often necessary for tasks like conditional rendering, dynamic content loading, or analytics tracking. This article will guide you through various methods to achieve this, catering to different scenarios and popular routing libraries. We'll explore using the browser's built-in window.location object, React Router's useLocation hook, and Next.js's usePathname hook, providing clear explanations and code examples for each approach. By the end, you'll be equipped to choose the most suitable method for accessing the current URL in your React projects.
There are several ways to get the current URL in your React application, depending on your use case and whether you're using a routing library like React Router or Next.js.
1. Using window.location
This is the most straightforward approach, using the browser's built-in window.location object.
function MyComponent() {
const currentURL = window.location.href;
return (
<div>
<p>The current URL is: {currentURL}</p>
</div>
);
}Explanation:
window.location.href provides the entire URL of the current page (including protocol, domain, path, and query parameters).2. Using React Router's useLocation Hook
If you're using React Router, the useLocation hook offers a more React-centric way to access location information.
import { useLocation } from 'react-router-dom';
function MyComponent() {
const location = useLocation();
return (
<div>
<p>Current path: {location.pathname}</p>
<p>Search query: {location.search}</p>
</div>
);
}Explanation:
useLocation hook from react-router-dom.useLocation() inside your component to get a location object.pathname (the path part of the URL) and search (the query string) from the location object.3. Using Next.js's usePathname Hook
In Next.js applications, the usePathname hook is the recommended way to get the current route path.
import { usePathname } from 'next/navigation';
function MyComponent() {
const pathname = usePathname();
return (
<div>
<p>Current path: {pathname}</p>
</div>
);
}Explanation:
usePathname hook from next/navigation.usePathname() inside your component to get the current route path as a string.Choosing the Right Approach:
window.location: Use for quick access to the full URL or specific parts like hostname, port, etc.useLocation: Best when working with React Router and you need detailed location information (path, search, state).usePathname: The preferred method within Next.js applications for accessing the current route path.The code provides three examples of how to get the current URL or path in a web application. The first example uses the browser's built-in window.location.href property. The second example uses the useLocation hook from the React Router library. The third example uses the usePathname hook from the Next.js framework. Each example shows how to display the current URL or path in a component.
// Example 1: Using window.location (no routing library)
function MyComponent() {
const currentURL = window.location.href;
return (
<div>
<h1>Current URL Example (window.location)</h1>
<p>The current URL is: {currentURL}</p>
</div>
);
}
// Example 2: Using React Router's useLocation hook
import { BrowserRouter, Routes, Route, Link, useLocation } from 'react-router-dom';
function RouterComponent() {
return (
<BrowserRouter>
<div>
<h1>React Router Example</h1>
<nav>
<ul>
<li>
<Link to="/">Home</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to="/about">About</Link>
</li>
<li>
<Link to="/contact?name=John&email=john@example.com">Contact</Link>
</li>
</ul>
</nav>
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<Home />} />
<Route path="/about" element={<About />} />
<Route path="/contact" element={<Contact />} />
</Routes>
</div>
</BrowserRouter>
);
}
function Home() {
return (
<div>
<h2>Home Page</h2>
</div>
);
}
function About() {
return (
<div>
<h2>About Page</h2>
</div>
);
}
function Contact() {
const location = useLocation();
return (
<div>
<h2>Contact Page</h2>
<p>Current path: {location.pathname}</p>
<p>Search query: {location.search}</p>
</div>
);
}
// Example 3: Using Next.js's usePathname hook (Next.js only)
// This example assumes you're in a Next.js component file
import { usePathname } from 'next/navigation';
function NextComponent() {
const pathname = usePathname();
return (
<div>
<h1>Next.js Example</h1>
<p>Current path: {pathname}</p>
</div>
);
}
// Render the examples (choose one or comment out the others)
ReactDOM.render(<MyComponent />, document.getElementById('root'));
// ReactDOM.render(<RouterComponent />, document.getElementById('root'));
// ReactDOM.render(<NextComponent />, document.getElementById('root')); Explanation:
window.location.href approach.useLocation within a React Router setup to get more detailed location information.usePathname hook in a Next.js component.Remember to choose the example that aligns with your project setup (whether you're using a routing library or not) and install the necessary dependencies (react-router-dom for React Router).
General Considerations:
window.location is only available in the browser (client-side). If you need to access the URL during server-side rendering (SSR) in Next.js or other frameworks, you'll need to use different techniques provided by those frameworks.encodeURIComponent and decodeURIComponent to handle special characters correctly.window.location is simple, using hooks like useLocation (React Router) and usePathname (Next.js) is generally more efficient within their respective frameworks. These hooks update your components reactively when the URL changes.Additional Use Cases:
useLocation to implement logic that runs before navigating to a different route (e.g., prompting the user to save changes).Beyond the Basics:
useNavigate (for programmatic navigation) and useParams (for accessing route parameters).By understanding these different approaches and their nuances, you can effectively work with URLs in your React applications, regardless of the routing library you choose.
This article provides a concise guide on obtaining the current URL within your React applications, outlining three primary methods:
| Method | Description | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
window.location |
Leverages the browser's built-in object to access the complete URL string. | Quick access to the full URL or specific components like hostname or port. |
React Router's useLocation hook |
Offers a React-centric approach for retrieving detailed location data. | Working within React Router applications and requiring access to path, search parameters, or state. |
Next.js's usePathname hook |
Provides the recommended method for fetching the current route path. | Specifically designed for use within Next.js applications. |
By understanding the strengths and ideal use cases of each approach, developers can choose the most suitable method for accessing the current URL within their React projects.
In conclusion, accessing the current URL in React applications is a straightforward process with multiple approaches available. The choice of method depends on the specific use case and the routing library being used. While window.location provides a quick and direct way to access the full URL, React Router's useLocation hook offers a more React-centric approach for detailed location information. In Next.js applications, the usePathname hook is the recommended choice for retrieving the current route path. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each method, developers can effectively manage URLs and implement dynamic features in their React applications.
 How to Get the Current Route or URL in React Router | Coding ... | Learn how to easily get the current route in React Router with this step-by-step guide. Improve your web app navigation today!
How to Get the Current Route or URL in React Router | Coding ... | Learn how to easily get the current route in React Router with this step-by-step guide. Improve your web app navigation today! Ways to Access React Get Current URL: A Comprehensive Guide | Learn how to access React get current URL in your application.
Ways to Access React Get Current URL: A Comprehensive Guide | Learn how to access React get current URL in your application..png) How to Read the Current full URL with React? - GeeksforGeeks | A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.
How to Read the Current full URL with React? - GeeksforGeeks | A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.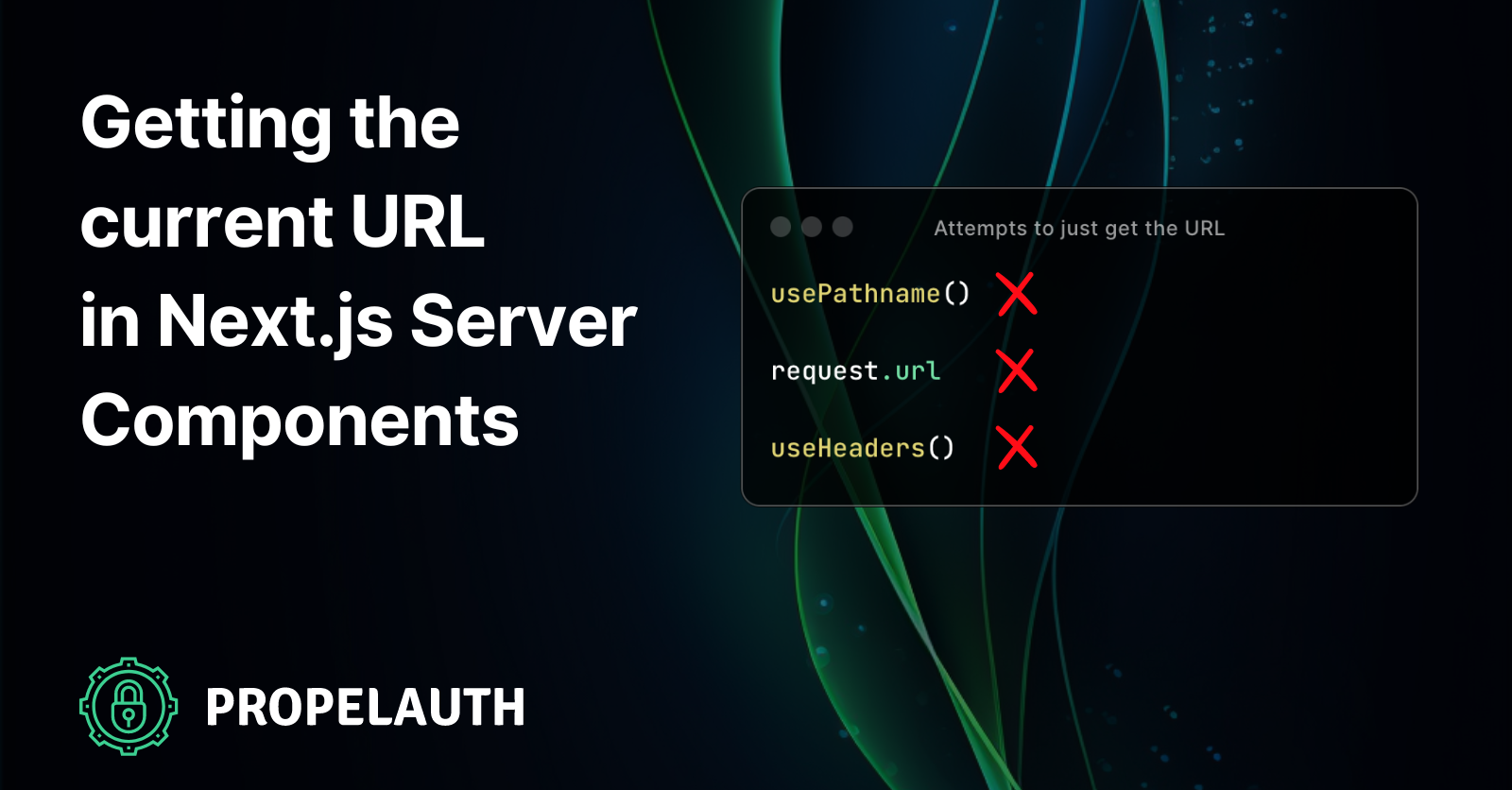 Getting the Current URL in Next.js Server Components | PropelAuth ... | You are writing a server component using the new(ish) App Router in Next.js, when you realize you need to get the current URL’s path. This could be for a sidebar, navbar, or even just breadcrumbs at the top of your page.
Getting the Current URL in Next.js Server Components | PropelAuth ... | You are writing a server component using the new(ish) App Router in Next.js, when you realize you need to get the current URL’s path. This could be for a sidebar, navbar, or even just breadcrumbs at the top of your page.Should be pretty easy, a quick
 How to get the current URL and pathname in React | Suraj Sharma | In this tutorial, I have discussed different ways to get the current URL and pathname in React - uselocation hook and window.location object
How to get the current URL and pathname in React | Suraj Sharma | In this tutorial, I have discussed different ways to get the current URL and pathname in React - uselocation hook and window.location object