Access GET request parameters in Express
Learn how to effortlessly access and utilize query string parameters in your Express.js application with our comprehensive guide.
Learn how to effortlessly access and utilize query string parameters in your Express.js application with our comprehensive guide.
This guide will help you learn how to extract information from URLs in Express.js. You will learn how to set up an Express.js project, define routes with parameters, access route parameters and query string parameters, handle POST requests and form data, and put it all together in a complete example.
Express.js, a popular Node.js framework, provides robust tools for handling HTTP requests and building web applications. A crucial aspect of this involves extracting information from URLs, encompassing both route parameters and query strings. Let's explore how to achieve this effectively:
1. Setting Up Your Express.js Project:
npm init -y. Install Express.js with the command:npm install expressapp.js) and set up a basic Express application:const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server listening on port ${port}`);
});2. Understanding Route Parameters:
app.get('/users/:userId', (req, res) => {
// Access the userId parameter
const userId = req.params.userId;
// ... further processing
});req.params. In the example above, req.params.userId would hold the value of the userId segment in the URL.3. Working with Query Strings:
Understanding Query Strings: Query strings are key-value pairs appended to the URL after a question mark (?). They are used to pass additional data to the server. For example: /search?q=keyword&category=electronics
Accessing Query String Parameters: Express.js provides the req.query object to access query string parameters:
app.get('/search', (req, res) => {
const searchQuery = req.query.q;
const category = req.query.category;
// ... use the query parameters
});4. Handling POST Requests and Form Data:
body-parser. Install it with:npm install body-parserbody-parser into your Express app:const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
app.post('/submit-form', (req, res) => {
const name = req.body.name;
const email = req.body.email;
// ... process form data
});5. Putting It All Together:
const express = require('express');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
app.get('/users/:userId', (req, res) => {
res.send(`User ID: ${req.params.userId}`);
});
app.get('/search', (req, res) => {
res.send(`Search query: ${req.query.q}, Category: ${req.query.category}`);
});
app.post('/submit-form', (req, res) => {
res.send(`Name: ${req.body.name}, Email: ${req.body.email}`);
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server listening on port ${port}`);
});This code demonstrates handling route parameters, query strings, and POST data in an Express.js application. Remember to adapt and expand upon these examples to suit your specific application requirements.
This Express.js code demonstrates URL information extraction. It sets up routes to handle URL parameters, query strings, and POST data from forms. The code includes explanations of each route and how it extracts information from the URL or request body. It also provides instructions on how to run the example.
This code demonstrates the concepts discussed in the article, allowing you to extract information from URLs in your Express.js application.
const express = require('express');
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const app = express();
const port = 3000;
// Middleware for parsing POST data
app.use(bodyParser.urlencoded({ extended: false }));
// Route with a parameter
app.get('/users/:userId', (req, res) => {
const userId = req.params.userId;
res.send(`You requested information for user with ID: ${userId}`);
});
// Route handling query strings
app.get('/search', (req, res) => {
const searchQuery = req.query.q;
const category = req.query.category;
res.send(`You searched for "${searchQuery}" in the "${category}" category.`);
});
// Route handling POST data from a form
app.post('/submit-form', (req, res) => {
const name = req.body.name;
const email = req.body.email;
res.send(`Welcome, ${name}! Your email is ${email}.`);
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Server is running on port ${port}`);
});Explanation:
express and body-parser modules.body-parser middleware is used to parse incoming POST request data./users/:userId route captures the userId from the URL.req.params.userId accesses the provided ID./search route expects query parameters q (search query) and category.req.query.q and req.query.category access the respective values./submit-form route handles form submissions (presumably using POST method).req.body.name and req.body.email access the submitted name and email.To run this example:
app.js).node app.js to start the server.Remember: This is a basic example. You can extend it to handle more complex scenarios and build robust web applications using Express.js.
Regular Expressions for Route Parameters: For more complex matching patterns in route parameters, you can use regular expressions. For example, app.get('/users/:userId([0-9]+)', ...) would only match user IDs that consist of numbers.
Middleware for Parameter Validation: Consider using middleware or custom functions to validate route parameters and query string values before processing them further. This helps ensure data integrity and prevent unexpected errors.
Error Handling: Implement proper error handling mechanisms to gracefully handle situations where route parameters or query string values are missing or invalid. You can use middleware or try-catch blocks within your route handlers.
Security Considerations: Be cautious when working with user-supplied data from URLs. Sanitize and validate input to prevent security vulnerabilities like SQL injection or cross-site scripting (XSS).
Alternative Routing Libraries: While Express.js provides basic routing capabilities, you might explore other routing libraries like Express Router or third-party options for more advanced features and flexibility.
API Design Best Practices: When designing APIs, consider using meaningful and consistent naming conventions for route parameters and query string keys. This enhances readability and maintainability of your code.
Documentation: Document your API endpoints clearly, specifying the expected format of URLs, route parameters, and query string parameters. This helps other developers understand how to interact with your application.
Testing: Thoroughly test your URL handling logic to ensure it functions as expected under various scenarios and edge cases. Use testing frameworks like Mocha or Jest to automate your tests.
Performance Optimization: For high-traffic applications, consider optimizing your URL parsing and routing logic to minimize processing overhead and improve response times.
URL Encoding and Decoding: Be mindful of URL encoding and decoding when working with special characters or spaces in route parameters or query string values. Use appropriate encoding/decoding functions to ensure data integrity.
Versioning: If your API is likely to evolve over time, consider implementing versioning in your URLs to maintain backward compatibility and avoid breaking changes for existing clients.
| Concept | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Setup | Install Express.js and create a basic app using express() and app.listen(). |
npm install express followed by creating an app.js file with basic setup. |
| Route Parameters | Define dynamic segments in URLs using : (e.g., /users/:userId). Access values with req.params. |
app.get('/users/:userId', ...) - access user ID with req.params.userId. |
| Query Strings | Key-value pairs after ? in URL (e.g., /search?q=keyword). Access with req.query. |
app.get('/search', ...) - access query with req.query.q. |
| POST Requests | Use body-parser middleware to handle data from HTML forms. Install with npm install body-parser. |
app.post('/submit-form', ...) - access form data with req.body.name. |
In conclusion, mastering the art of extracting information from URLs in Express.js empowers you to build dynamic and interactive web applications. By effectively utilizing route parameters, query strings, and handling POST data, you can create robust APIs and user interfaces that respond to diverse user inputs and requests. Remember to prioritize security, validation, and best practices to ensure the reliability and maintainability of your applications. As you delve deeper into Express.js and explore its capabilities, you'll discover even more sophisticated techniques for URL handling and routing, enabling you to create truly exceptional web experiences.
 How To Retrieve URL and POST Parameters with Express ... | Learn how to retrieve URL parameters and POST parameters from requests with Express.
How To Retrieve URL and POST Parameters with Express ... | Learn how to retrieve URL parameters and POST parameters from requests with Express. Get Query Strings and Parameters in Express.js | We'll be going over how to extract information from a URL in Express.js. Specifically, how do we extract information from a query string and how do we extract...
Get Query Strings and Parameters in Express.js | We'll be going over how to extract information from a URL in Express.js. Specifically, how do we extract information from a query string and how do we extract... How to receive post parameter in Express.js ? - GeeksforGeeks | A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions.
How to receive post parameter in Express.js ? - GeeksforGeeks | A Computer Science portal for geeks. It contains well written, well thought and well explained computer science and programming articles, quizzes and practice/competitive programming/company interview Questions. Access to query parameters without using Express - Glitch Help ... | I know that I have access to the URL’s query parameters if I use express. But I have a simple script that just uses console.log for output. Is there a way for such scripts to gain access to the query parameters? Thanks, Larry
Access to query parameters without using Express - Glitch Help ... | I know that I have access to the URL’s query parameters if I use express. But I have a simple script that just uses console.log for output. Is there a way for such scripts to gain access to the query parameters? Thanks, Larry Express routing | get() to handle GET requests and app.post to ... Route parameters. Route parameters are named URL segments ... Use the express.Router class to create modular ...
Express routing | get() to handle GET requests and app.post to ... Route parameters. Route parameters are named URL segments ... Use the express.Router class to create modular ...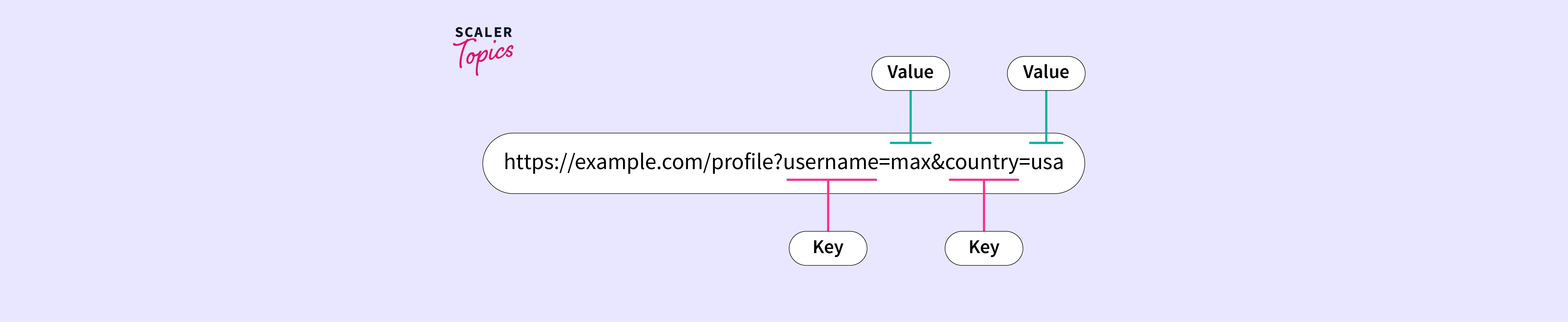 Query Parameter in Express - Scaler Topics | This article on Scaler Topics covers Query Parameter in Express in Express JS with examples, explanations, and use cases, read to know more.
Query Parameter in Express - Scaler Topics | This article on Scaler Topics covers Query Parameter in Express in Express JS with examples, explanations, and use cases, read to know more. Access GET parameters in Express on Node.js | Sentry | The Problem How do I access GET parameters in a URL's query string in a Node.js Express application? The Solution We can access the GET parameters of the…
Access GET parameters in Express on Node.js | Sentry | The Problem How do I access GET parameters in a URL's query string in a Node.js Express application? The Solution We can access the GET parameters of the…