Solidity: Initializing Arrays Within Structs
Learn how to initialize an array within a struct using Solidity, a popular programming language for smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain.
Learn how to initialize an array within a struct using Solidity, a popular programming language for smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain.
In Solidity, structs and arrays are essential data structures that allow you to organize and manage complex data within your smart contracts. This guide will walk you through the process of defining structs, creating arrays of structs, and adding elements to these arrays.
Define the struct:
struct Payment {
uint amount;
address sender;
}Declare an array of structs:
Payment[] public payments;Add elements to the array:
payments.push(Payment({ amount: 100, sender: msg.sender }));Key Points:
push() to add elements dynamically.This Solidity code defines a simple contract for recording payments. It uses a struct to represent individual payments, each storing the payment amount and sender's address. Payments are stored in a dynamically sized array. The contract provides functions to make a payment, get the total payment count, and retrieve details of a specific payment using its index.
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract PaymentContract {
// Define the Payment struct
struct Payment {
uint amount;
address sender;
}
// Declare an array of Payment structs
Payment[] public payments;
// Function to add a new payment to the array
function makePayment(uint _amount) public {
payments.push(Payment({ amount: _amount, sender: msg.sender }));
}
// Function to get the total number of payments
function getPaymentCount() public view returns (uint) {
return payments.length;
}
// Function to get the details of a specific payment
function getPayment(uint _index) public view returns (uint, address) {
require(_index < payments.length, "Payment index out of bounds");
Payment memory payment = payments[_index];
return (payment.amount, payment.sender);
}
}Explanation:
Struct Definition: We define a struct named Payment to represent a single payment, containing the amount and the sender's address.
Array Declaration: We declare a public state variable payments as an array of Payment structs. The public keyword automatically generates a getter function for the array.
Adding Elements: The makePayment function takes an _amount as input and creates a new Payment struct. It then uses push() to append this new payment to the payments array.
Helper Functions:
getPaymentCount returns the total number of payments recorded.getPayment allows retrieving details of a specific payment using its index in the array.Key Points Illustrated:
payments array doesn't need a predefined size; it grows dynamically using push().Payment to the array, we provide values for both amount and sender.getPayment function demonstrates using a memory struct variable to temporarily hold the payment data for efficient access.This example provides a basic framework for managing payments using structs and arrays in Solidity. You can extend it further by adding more complex logic, such as handling different payment types, tracking payment statuses, or implementing withdrawal mechanisms.
Structs:
struct keyword followed by the struct name and a code block defining its members.uint, address, bool, other structs, etc.).Arrays of Structs:
Payment[] public payments;).payments[0].amount).Storage vs. Memory:
memory struct variable to temporarily hold data when reading from storage, as seen in the getPayment function example.Other Considerations:
Example Use Cases:
username, email, and reputation.name, price, and quantity.rarity, level, and owner.This article explains how to use arrays of structs in Solidity. Here's a breakdown:
1. Defining Structs:
Payment struct storing amount and sender information.2. Declaring Struct Arrays:
Payment[] public payments; declares a public array named payments that stores Payment structs.3. Adding Elements:
push() function to dynamically add elements to the array.payments.push(Payment({ amount: 100, sender: msg.sender })); adds a new Payment struct to the payments array.Key Takeaways:
push() to add elements, expanding the array automatically.Understanding structs and arrays is crucial for organizing data effectively in your Solidity contracts. Structs allow you to create custom data types for grouping related information, while arrays provide a way to manage collections of these structs. By mastering these concepts, you can build more sophisticated and well-structured smart contracts. Remember to consider gas optimization and choose the appropriate data structures based on your specific needs. As you delve deeper into Solidity, exploring advanced concepts like mappings and dynamic arrays will further enhance your ability to build powerful and efficient decentralized applications.
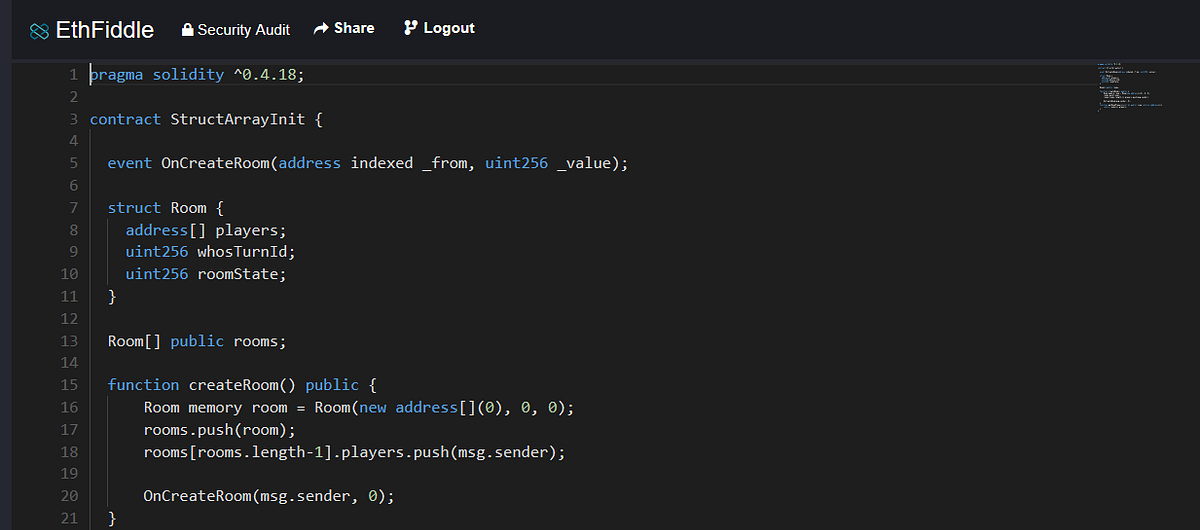 Ethereum Solidity: Memory vs Storage & How to initialize an array ... | In Loom Network’s Telegram (which has ~8,000 members!) people ask questions on various topics such as Loom’s roadmap, theoretical…
Ethereum Solidity: Memory vs Storage & How to initialize an array ... | In Loom Network’s Telegram (which has ~8,000 members!) people ask questions on various topics such as Loom’s roadmap, theoretical… Initializing an Array Inside a Struct in Solidity - | In Solidity, structs allow developers to define custom data types composed of multiple fields. These fields can include arrays.
Initializing an Array Inside a Struct in Solidity - | In Solidity, structs allow developers to define custom data types composed of multiple fields. These fields can include arrays. Feature request: auto-infer the type when pushing to an array of structs | Given a struct like this: struct Set { uint256 x; uint256 y; uint256 expected; } It is possible to initialize an instance using a key-value mapping, like this: Set mySet = Set({ x: 1, y: 2, expected: 3 }); Which is really nice. Now, suppose that you have an array of structs, defined in the storage of a contract: contract Foo { Set[] internal sets; } To append an element to the array, we can do this: sets.push(Set({ x: 1, y: 2, expected: 3 })); Here’s my feature request -...
Feature request: auto-infer the type when pushing to an array of structs | Given a struct like this: struct Set { uint256 x; uint256 y; uint256 expected; } It is possible to initialize an instance using a key-value mapping, like this: Set mySet = Set({ x: 1, y: 2, expected: 3 }); Which is really nice. Now, suppose that you have an array of structs, defined in the storage of a contract: contract Foo { Set[] internal sets; } To append an element to the array, we can do this: sets.push(Set({ x: 1, y: 2, expected: 3 })); Here’s my feature request -... Types — Solidity 0.8.29 documentation | Array elements can be of any type, including mapping or struct. The general ... If you want to initialize dynamically-sized arrays, you have to assign the ...
Types — Solidity 0.8.29 documentation | Array elements can be of any type, including mapping or struct. The general ... If you want to initialize dynamically-sized arrays, you have to assign the ...