Find kubeadm join command on master node
Learn how to easily locate the kubeadm join command on your Kubernetes master node for adding worker nodes to your cluster.
Learn how to easily locate the kubeadm join command on your Kubernetes master node for adding worker nodes to your cluster.
To add a new node to your Kubernetes cluster, you'll need a special join command from your master node. This command contains a unique token that acts like a key, allowing the new node to securely join the cluster. Here's how to get and use this join command:
To join a node to your Kubernetes cluster, you'll need the join command generated on your master node. Here's how to get it:
1. On your master node:
kubeadm token create --print-join-commandThis command does two things:
2. Copy the entire join command output.
3. On the node you want to join:
This process ensures secure communication and authentication between the new node and your existing Kubernetes cluster.
This guide explains how to add a new node to an existing Kubernetes cluster. On the master node, generate a join command using 'kubeadm token create --print-join-command'. Copy the entire command output. On the node you want to add, paste and run the copied join command. Ensure the new node can communicate with the master node and that the master node was previously set up with 'kubeadm init'. This process securely integrates the new node into your cluster.
This example demonstrates how to join a node to your Kubernetes cluster.
1. On your master node:
kubeadm token create --print-join-commandThis command will output something similar to:
kubeadm join <master-node-ip>:<port> --token <token> \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:<hash>
2. Copy the entire join command output.
3. On the node you want to join:
kubeadm join 192.168.0.100:6443 --token abcdef.0123456789abcdef \
--discovery-token-ca-cert-hash sha256:1234567890abcdef1234567890abcdef1234567890abcdef1234567890abcdef Important Notes:
<master-node-ip>, <port>, <token>, and <hash> with the actual values from your output.kubeadm init.This process securely adds the new node to your cluster, allowing it to participate in the Kubernetes environment.
--usages flag when creating it.kubeadm token list.kubeadm token delete <token>.kubelet logs on the joining node are particularly helpful for debugging join issues.| Step | Action | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1. On Master Node | Run: kubeadm token create --print-join-command
|
* Generates a unique token: Acts as a key for the joining node. * Prints the join command: Includes the generated token. |
| 2. On Master Node | Copy the entire join command output. | |
| 3. On Joining Node | Paste and run the copied join command. | This securely adds the node to the cluster. |
Joining nodes to your Kubernetes cluster is a fundamental process, made simple and secure with kubeadm. By generating a join command on the master node and executing it on the node you wish to add, you can easily expand your cluster's resources and capabilities. Remember to pay attention to security best practices, such as keeping tokens confidential and configuring firewalls appropriately. With a solid understanding of these steps, you'll be well-equipped to manage and scale your Kubernetes cluster effectively.
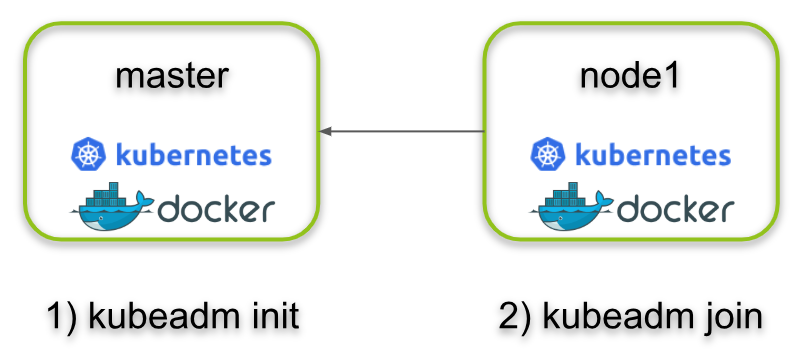 Regenerate Kubernetes Join Command to Join Work Node | by Yst ... | When we first init a K8S cluster, it will output the join command for us to join work node shown as below. But the token, by default, is…
Regenerate Kubernetes Join Command to Join Work Node | by Yst ... | When we first init a K8S cluster, it will output the join command for us to join work node shown as below. But the token, by default, is… kubeadm join | Kubernetes | This command initializes a new Kubernetes node and joins it to the existing cluster.
Run this on any machine you wish to join an existing cluster
Synopsis When joining a kubeadm initialized cluster, we need to establish bidirectional trust. This is split into discovery (having the Node trust the Kubernetes Control Plane) and TLS bootstrap (having the Kubernetes Control Plane trust the Node).
There are 2 main schemes for discovery.
kubeadm join | Kubernetes | This command initializes a new Kubernetes node and joins it to the existing cluster.
Run this on any machine you wish to join an existing cluster
Synopsis When joining a kubeadm initialized cluster, we need to establish bidirectional trust. This is split into discovery (having the Node trust the Kubernetes Control Plane) and TLS bootstrap (having the Kubernetes Control Plane trust the Node).
There are 2 main schemes for discovery. Not able to join node to Master - General Discussions - Discuss ... | Hello, I am not able to join Node to Kubernetes master. Earlier I was able to join node to master but I had some issues on master , so I had to reset it. I reset it by using kubeadm reset command and was able to successfully access Kubernetes dashboard. However, when I am trying to join node to master, I am getting the following error- error execution phase preflight couldn’t validate the identity of the api server: abort connecting to API servers after timeout of 5m0s I have also tried to r...
Not able to join node to Master - General Discussions - Discuss ... | Hello, I am not able to join Node to Kubernetes master. Earlier I was able to join node to master but I had some issues on master , so I had to reset it. I reset it by using kubeadm reset command and was able to successfully access Kubernetes dashboard. However, when I am trying to join node to master, I am getting the following error- error execution phase preflight couldn’t validate the identity of the api server: abort connecting to API servers after timeout of 5m0s I have also tried to r... Kubernetes — Create a new token and join command to rejoin/add ... | In this tutorial I will go through for creating a new token before adding a node to the Kubernetes cluster.
Kubernetes — Create a new token and join command to rejoin/add ... | In this tutorial I will go through for creating a new token before adding a node to the Kubernetes cluster.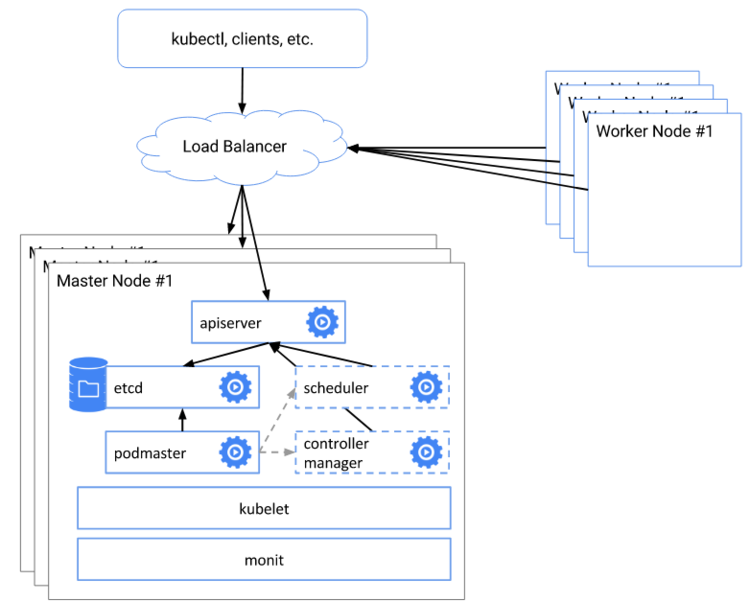 Highly Available Kubernetes Cluster using kubeadm | Save the new master and worker node join commands with the token. Join the second master node to the control plane using the join command. Join the worker nodes ...
Highly Available Kubernetes Cluster using kubeadm | Save the new master and worker node join commands with the token. Join the second master node to the control plane using the join command. Join the worker nodes ...