Docker ENTRYPOINT vs Kubernetes COMMAND: Key Differences Explained
Learn the key differences between Docker ENTRYPOINT and Kubernetes container spec COMMAND for efficient container deployment and orchestration.
Learn the key differences between Docker ENTRYPOINT and Kubernetes container spec COMMAND for efficient container deployment and orchestration.
Understanding how Docker and Kubernetes handle container startup commands is crucial for building and deploying applications effectively. This involves using ENTRYPOINT and CMD in your Dockerfiles and understanding how Kubernetes interacts with these instructions through command and args in Pod definitions. This interplay allows for flexibility in development and precise control in deployment.
Dockerfile Basics: In a Dockerfile, you use ENTRYPOINT to define the main command a container executes when it starts. CMD provides default arguments for that command.
ENTRYPOINT ["my_app"]
CMD ["--arg1", "value1"] Kubernetes Interaction: When you deploy a container to Kubernetes using a Pod, you can use command and args in your Pod definition.
Overriding Behavior: Kubernetes command completely replaces the Dockerfile ENTRYPOINT. args in Kubernetes replaces the Dockerfile CMD.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
spec:
containers:
- name: my-container
image: my-image:latest
command: ["my_other_app"]
args: ["--new-arg", "new-value"] Use Cases:
ENTRYPOINT for Executables: Use ENTRYPOINT when your container is essentially a wrapper around an executable (e.g., a database server).CMD for Flexibility: Use CMD for default arguments that you might want to change easily when running the container with docker run or in Kubernetes.command and args to precisely control how your container starts, potentially overriding the Dockerfile settings for specific deployments.This code example illustrates how Dockerfile ENTRYPOINT and CMD instructions interact with Kubernetes Pod command and args configurations. It provides a Dockerfile that sets up a container with a default command and arguments, and a Kubernetes Pod definition that overrides these defaults. The example explains how this override mechanism allows for flexibility in container execution within a Kubernetes environment.
This example demonstrates the interaction between Dockerfile ENTRYPOINT/CMD and Kubernetes Pod command/args.
1. Dockerfile (Dockerfile)
FROM alpine:latest
# Install a simple application (replace with your own)
RUN apk add --no-cache figlet
# Define the entrypoint - the main command
ENTRYPOINT ["figlet"]
# Define default arguments for figlet
CMD ["Hello from Docker!"] 2. Kubernetes Pod Definition (pod.yaml)
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: my-pod
spec:
containers:
- name: my-container
image: my-image:latest # Built from the Dockerfile above
# Kubernetes command overrides Dockerfile ENTRYPOINT
command: ["echo"]
# Kubernetes args override Dockerfile CMD
args: ["Hello from Kubernetes!"] Explanation:
Dockerfile: This Dockerfile sets up a container that runs the figlet command by default. If you build this image and run it with docker run, it will output "Hello from Docker!" in a stylized font.
Kubernetes Pod: This Pod definition uses the image built from the Dockerfile. However, it overrides the default behavior:
command: ["echo"]: The container will now execute the echo command instead of figlet.args: ["Hello from Kubernetes!"]: The container will echo "Hello from Kubernetes!" instead of the Dockerfile's default message.Use Cases:
ENTRYPOINT for an executable (figlet).CMD to provide default arguments that can be easily changed.Running the Example:
docker build -t my-image:latest .
kubectl apply -f pod.yaml
kubectl logs my-pod
You should see "Hello from Kubernetes!" in the logs, demonstrating the overrides.
General:
ENTRYPOINT, CMD) and your Kubernetes Pod definition (command, args) to identify any mismatches or unintended overrides. Kubernetes logs can be invaluable here.ENTRYPOINT and CMD can be used in "shell form" (e.g., CMD echo "Hello") or "exec form" (e.g., CMD ["echo", "Hello"]). Exec form is generally preferred for clarity and avoiding potential issues with shell interpretation.Dockerfile:
ENTRYPOINT for Processes: Think of ENTRYPOINT as defining what your container is. If your container's primary purpose is to run a specific application, ENTRYPOINT is the place to specify it.CMD for Defaults and Overrides: CMD is more flexible. It's useful for providing default settings that can be easily changed at runtime, either through docker run commands or, more importantly, through Kubernetes configurations.Kubernetes:
command and args give you fine-grained control over container startup. This is particularly useful in deployment scenarios where you might need to adjust the container's behavior without rebuilding the image.Best Practices:
By understanding these nuances and following best practices, you can ensure that your Docker containers start up correctly and reliably within your Kubernetes deployments.
| Feature | Dockerfile | Kubernetes Pod Definition | Overriding Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| Main Command |
ENTRYPOINT defines the executable. |
command defines the executable. |
Kubernetes command replaces Dockerfile ENTRYPOINT. |
| Command Arguments |
CMD provides default arguments. |
args provides arguments. |
Kubernetes args replaces Dockerfile CMD. |
Key Points:
ENTRYPOINT for the primary executable and CMD for default arguments that can be easily overridden.command and args to customize container startup, even overriding Dockerfile settings.Understanding the interplay between Dockerfile instructions (ENTRYPOINT, CMD) and Kubernetes Pod configurations (command, args) is essential for building and deploying containerized applications effectively. Dockerfiles provide a way to define the default execution behavior of a container, while Kubernetes configurations offer flexibility and control over how containers start within a cluster. By mastering these concepts, developers can ensure that their applications are deployed consistently and reliably in a Kubernetes environment.
 Define a Command and Arguments for a Container | Kubernetes | This page shows how to define commands and arguments when you run a container in a Pod.
Before you begin You need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. It is recommended to run this tutorial on a cluster with at least two nodes that are not acting as control plane hosts. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using minikube or you can use one of these Kubernetes playgrounds:
Define a Command and Arguments for a Container | Kubernetes | This page shows how to define commands and arguments when you run a container in a Pod.
Before you begin You need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the kubectl command-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. It is recommended to run this tutorial on a cluster with at least two nodes that are not acting as control plane hosts. If you do not already have a cluster, you can create one by using minikube or you can use one of these Kubernetes playgrounds: Docker Entrypoint Vs CMD and Kubernetes - iGreenData | Docker gives two ways of running the main process ENTRYPOINT and CMD. I’ve seen lot of confusion about these options. Both can be used to tell docker what should be executed to run main process - so what should you be using. Is one better than other ? Can you use both ? Kubernetes uses
Docker Entrypoint Vs CMD and Kubernetes - iGreenData | Docker gives two ways of running the main process ENTRYPOINT and CMD. I’ve seen lot of confusion about these options. Both can be used to tell docker what should be executed to run main process - so what should you be using. Is one better than other ? Can you use both ? Kubernetes uses Dockerfile ENTRYPOINT vs CMD and how Kubernetes handles it ... | Demystify Dockerfile ENTRYPOINT and CMD commands
Dockerfile ENTRYPOINT vs CMD and how Kubernetes handles it ... | Demystify Dockerfile ENTRYPOINT and CMD commands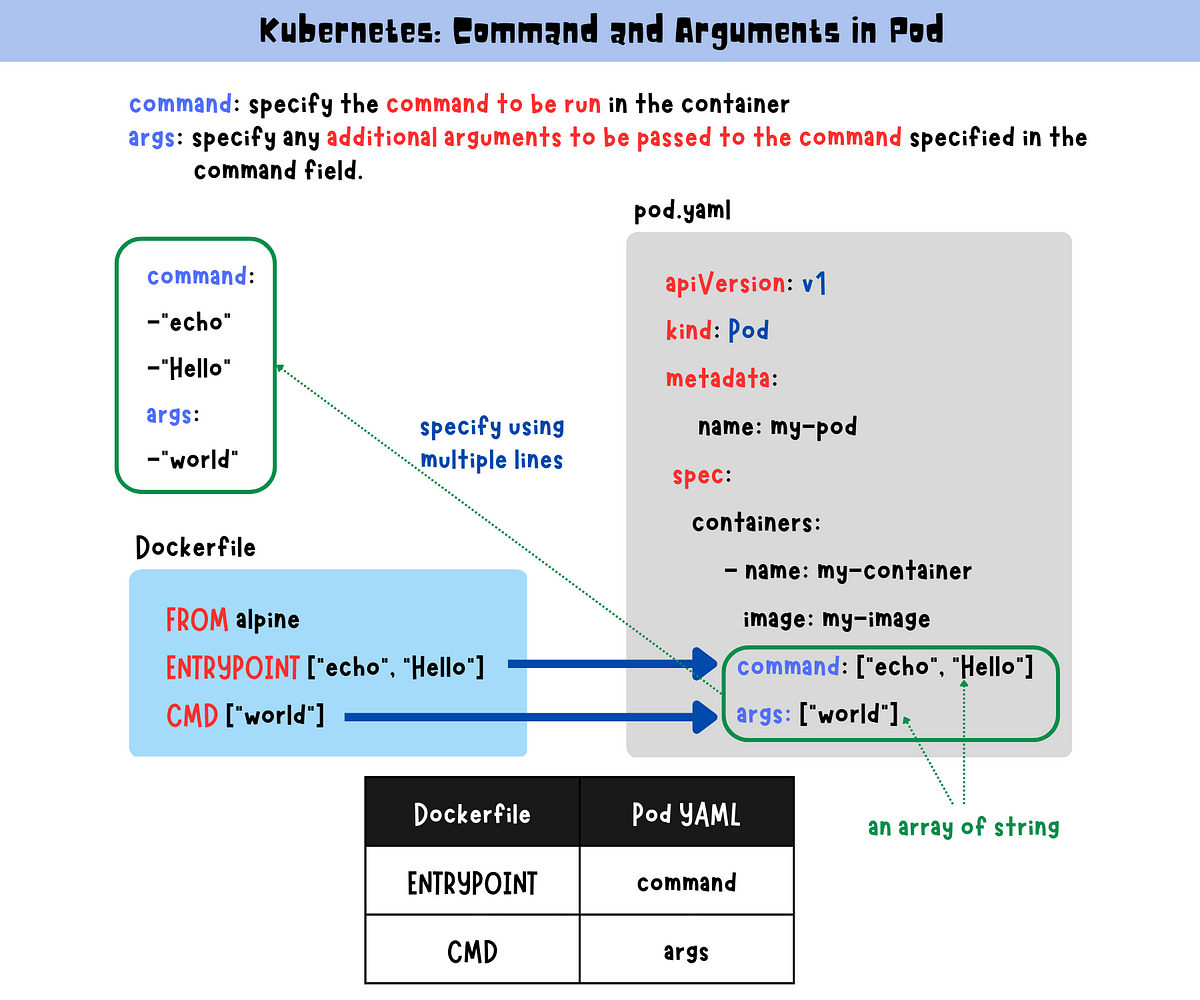 Kubernetes: Command and Arguments in Pod | by Claire Lee ... | The command and args fields in Kubernetes Pod YAML files specify the command to be run in the container and any additional arguments to be…
Kubernetes: Command and Arguments in Pod | by Claire Lee ... | The command and args fields in Kubernetes Pod YAML files specify the command to be run in the container and any additional arguments to be… Understanding CMD and ENTRYPOINT Differences in Docker | Learn the differences between CMD and ENTRYPOINT in Docker, their use cases, and how to work with them. Get hands-on insights with examples from Devtron.
Understanding CMD and ENTRYPOINT Differences in Docker | Learn the differences between CMD and ENTRYPOINT in Docker, their use cases, and how to work with them. Get hands-on insights with examples from Devtron. Docker CMD vs. ENTRYPOINT: What's the Difference and How to ... | Mar 8, 2024 ... CMD. Sets default parameters that can be overridden from the Docker Command Line Interface (CLI) when a container is running. ENTRYPOINT.
Docker CMD vs. ENTRYPOINT: What's the Difference and How to ... | Mar 8, 2024 ... CMD. Sets default parameters that can be overridden from the Docker Command Line Interface (CLI) when a container is running. ENTRYPOINT. Docker ENTRYPOINT Vs CMD Explained With Examples | In this blog we will look at the key differences between Docker ENTRYPOINT vs CMD instruction using a
Docker ENTRYPOINT Vs CMD Explained With Examples | In this blog we will look at the key differences between Docker ENTRYPOINT vs CMD instruction using a