AWS ASG Launch Templates vs Configurations: Key Differences
Learn about the key differences between AWS ASG Launch Templates and Launch Configurations to determine the best fit for your cloud infrastructure needs.
Learn about the key differences between AWS ASG Launch Templates and Launch Configurations to determine the best fit for your cloud infrastructure needs.
When working with Amazon EC2, especially within the context of Auto Scaling Groups, understanding how your instances are launched and configured is crucial. This involves using either Launch Configurations or Launch Templates, both of which act as blueprints for your EC2 instances. This article will delve into the differences between these two methods, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses to help you make informed decisions for your AWS environment.
Launch Configurations and Launch Templates: These are AWS features that define how your EC2 instances are set up when they're launched, especially within Auto Scaling Groups. Think of them as blueprints for your instances.
Launch Configurations: These were introduced first. They let you specify things like the AMI (Amazon Machine Image) to use, instance type, security groups, and key pairs. However, they have a limitation: once you create a Launch Configuration, you can't modify it. You need to create a new one with the desired changes.
Launch Templates: These are the newer, more flexible option. They offer all the features of Launch Configurations but with a key advantage: they are mutable. This means you can update a Launch Template directly without creating a new one.
Key Differences:
Migration: AWS recommends moving from Launch Configurations to Launch Templates for the added flexibility and features. You can migrate existing Auto Scaling Groups to use Launch Templates.
When to Use What:
In Summary: Launch Templates are the successor to Launch Configurations, providing a more modern and flexible way to manage your EC2 instance configurations in AWS.
This Python code demonstrates how to create and use an AWS Launch Template using the Boto3 library. It defines a template configuration including AMI ID, instance type, key pair, and security groups. The code then shows how to create a Launch Template, optionally update it, and finally use it to launch instances within an Auto Scaling Group. Placeholder values are used for demonstration purposes and should be replaced with actual AWS resource IDs.
This example demonstrates how to create and use a Launch Template in AWS using the AWS SDK for Python (Boto3).
Prerequisites:
pip install boto3)Code:
import boto3
# Create an EC2 client
ec2 = boto3.client('ec2')
# Define Launch Template data
launch_template_name = 'MyLaunchTemplate'
image_id = 'ami-0c55b159c9009b8b5' # Replace with your desired AMI ID
instance_type = 't2.micro'
key_name = 'your-key-pair-name' # Replace with your key pair name
# Create the Launch Template
response = ec2.create_launch_template(
LaunchTemplateName=launch_template_name,
LaunchTemplateData={
'ImageId': image_id,
'InstanceType': instance_type,
'KeyName': key_name,
'SecurityGroupIds': [
'sg-0123456789abcdef0', # Replace with your security group ID
],
}
)
launch_template_id = response['LaunchTemplate']['LaunchTemplateId']
print(f"Launch Template created with ID: {launch_template_id}")
# --- Optional: Update the Launch Template ---
# ec2.modify_launch_template(
# LaunchTemplateId=launch_template_id,
# LaunchTemplateData={
# 'InstanceType': 't2.medium' # Update instance type
# }
# )
# print("Launch Template updated.")
# --- Create an Auto Scaling Group using the Launch Template ---
autoscaling = boto3.client('autoscaling')
response = autoscaling.create_auto_scaling_group(
AutoScalingGroupName='MyAutoScalingGroup',
LaunchTemplate={
'LaunchTemplateId': launch_template_id,
'Version': '$Latest' # Use the latest version of the Launch Template
},
MinSize=1,
MaxSize=3,
AvailabilityZones=[
'us-east-1a',
'us-east-1b'
]
)
print("Auto Scaling Group created using the Launch Template.")Explanation:
This code demonstrates the basic usage of Launch Templates. You can further customize the Launch Template data and Auto Scaling Group configuration based on your specific needs. Remember to replace the placeholder values with your actual AWS resources.
By understanding the differences and use cases for Launch Configurations and Launch Templates, you can streamline your EC2 instance management and ensure your applications are deployed efficiently and reliably on AWS.
| Feature | Launch Configuration | Launch Template |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Define EC2 instance setup at launch | Define EC2 instance setup at launch |
| Mutability | Immutable (cannot be modified) | Mutable (can be updated directly) |
| Versioning | Not supported | Supported |
| Flexibility | Limited | More advanced features (e.g., multiple instance types) |
| Recommendation | Use for existing setups only | Preferred choice for new setups |
Summary:
Launch Templates are the recommended method for defining EC2 instance configurations in AWS. They offer greater flexibility and control compared to Launch Configurations, including the ability to update configurations, track versions, and utilize advanced features. While Launch Configurations are still supported, AWS recommends migrating to Launch Templates for new setups.
In conclusion, AWS Launch Templates have emerged as the preferred method for defining EC2 instance configurations, offering significant advantages over their predecessor, Launch Configurations. Their mutable nature, versioning support, and advanced features like multiple instance type specification provide greater flexibility and control over instance deployments. While Launch Configurations remain supported for existing setups, migrating to Launch Templates is highly recommended for new AWS deployments to leverage these benefits and streamline EC2 instance management. By understanding the key differences and use cases for both methods, users can make informed decisions to optimize their cloud infrastructure and ensure efficient and reliable application deployments on AWS.
 Auto Scaling launch templates - Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling | A launch template is similar to a launch configuration, in that it specifies instance configuration information. It includes the ID of the Amazon Machine ...
Auto Scaling launch templates - Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling | A launch template is similar to a launch configuration, in that it specifies instance configuration information. It includes the ID of the Amazon Machine ... Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling will no longer add support for new EC2 ... | This post is written by Scott Horsfield, Principal Solutions Architect, EC2 Scalability and Surabhi Agarwal, Sr. Product Manager, EC2. In 2010, AWS released launch configurations as a way to define the parameters of instances launched by EC2 Auto Scaling groups. In 2017, AWS released launch templates, the successor of launch configurations, as a way to streamline […]
Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling will no longer add support for new EC2 ... | This post is written by Scott Horsfield, Principal Solutions Architect, EC2 Scalability and Surabhi Agarwal, Sr. Product Manager, EC2. In 2010, AWS released launch configurations as a way to define the parameters of instances launched by EC2 Auto Scaling groups. In 2017, AWS released launch templates, the successor of launch configurations, as a way to streamline […]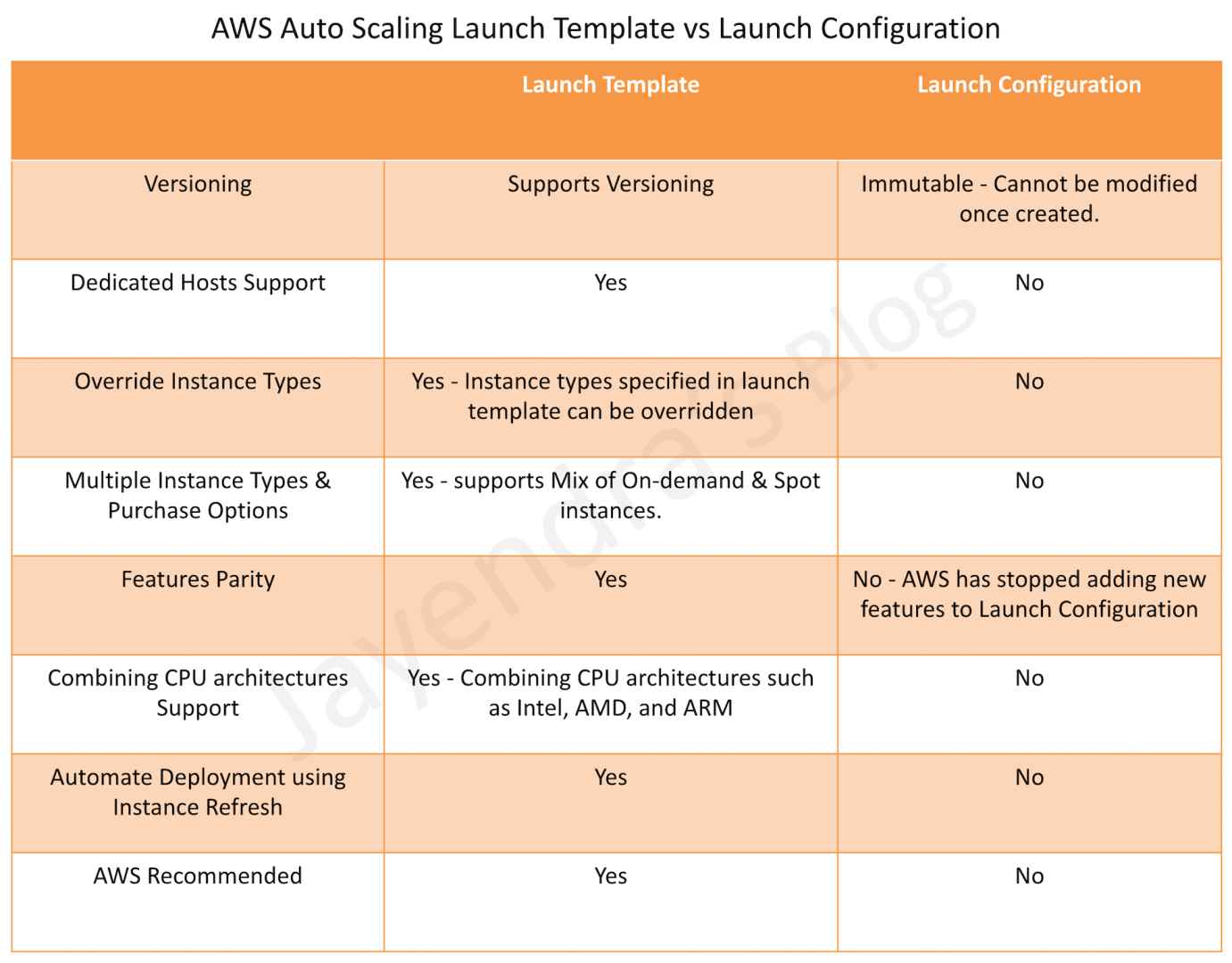 AWS Auto Scaling Launch Template vs Launch Configuration | Launch Template vs Launch Configuration compares the various aspects of similarities and enhancements between the features.
AWS Auto Scaling Launch Template vs Launch Configuration | Launch Template vs Launch Configuration compares the various aspects of similarities and enhancements between the features. Launch Template vs Launch Configuration and How to Migrate | Learn about the difference between launch template vs launch configuration and find out how to migrate from configurations to templates with our guide.
Launch Template vs Launch Configuration and How to Migrate | Learn about the difference between launch template vs launch configuration and find out how to migrate from configurations to templates with our guide. Understanding the Differences between AWS Launch Configuration ... | Regarding launching instances in Amazon Web Services (AWS), there are two main options to choose from: Launch Configuration and Launch…
Understanding the Differences between AWS Launch Configuration ... | Regarding launching instances in Amazon Web Services (AWS), there are two main options to choose from: Launch Configuration and Launch… AWS – EC2 Launch Configuration vs Launch Templates - BDRSuite | Table of Contents What is Launch Configuration? What is Launch Templates? Advantages of Launch Templates Creating an EC2 Launch Template Conclusion In this article we will discuss the difference between AWS EC2 Launch Configuration and Launch Template, and how they work. Also, we will look […]
AWS – EC2 Launch Configuration vs Launch Templates - BDRSuite | Table of Contents What is Launch Configuration? What is Launch Templates? Advantages of Launch Templates Creating an EC2 Launch Template Conclusion In this article we will discuss the difference between AWS EC2 Launch Configuration and Launch Template, and how they work. Also, we will look […] Cannot switch one Autoscaling group from launch configuration to ... | I have almost finished converting all of my Autoscaling groups from launch configurations to launch templates, but am stuck at one autoscaling group in eu-north-1.
Cannot switch one Autoscaling group from launch configuration to ... | I have almost finished converting all of my Autoscaling groups from launch configurations to launch templates, but am stuck at one autoscaling group in eu-north-1.When I click the "Switch to laun...